Traveling Backward: De-differentiation to Stemness
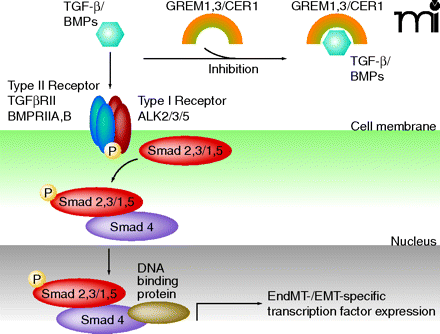
The BMP/TGF-β signaling pathway and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway can be inhibited by gremlins GREM1/3 or Cerberus 1(CER1) through heterodimer formation with ligands of the TGF-β/BMP family and prevention of TGF-β/BMP type II receptor/ligand interaction (25). Following TGF-β or BMP ligand binding and according phosphorylation activation of their corresponding type II signaling receptors, type I signaling receptors including receptors of the ALK family are phosphorylation activated and promote phosphorylation of Smad2,3 (TGF-β) or Smad1,5 (BMPs), respectively. Binding of phosphorylation-activated Smad2,3/Smad1,5 to Smad4 enables nuclear translocation and transcriptional activation of EndMT-associated transcription factors, via other DNA-binding co-factors. [Adapted with modifications from (26, 27)].



