Matters of the Heart: The Case of TNFα-Targeting Drugs
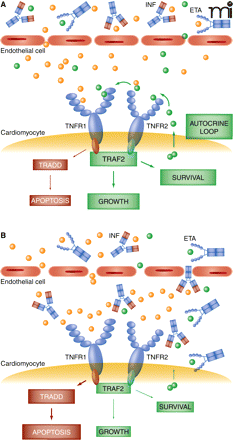
Figure 2
Proposed mechanism for cardiac protection by low TNFα and cardiac toxicity by anti-TNFα
A. Cardiomyocytes may synthetize and release discrete amounts of TNFα that bind to TNFR2 and eventually pass to TNFR1, activating survival-oriented cell responses that protect against higher levels of TNFα. B. Penetration of anti-TNFα drugs through discontinuous endothelium of the failing heart interrupts the autocrine loop and eventually shifts TNFR1–2 to signaling apoptosis. Solid blue circles represent circulating TNFα; solid green circles represent TNFα released by cardiomyocytes. INF, infliximab; ETA, etanercept; TNFR1–2, TNFα receptor 1–2; TRAF2, TNFα receptor–associated factor 2; TRADD, TNFR1-associated death domain.



