
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Small Interfering RNAs: A Revolutionary Tool for the Analysis of Gene Function and Gene Therapy
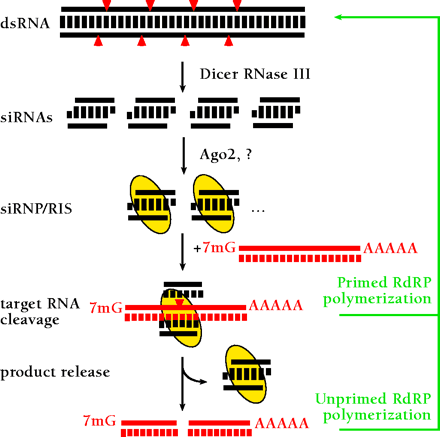
A model for RNA interference. dsRNA is processed to 21- to 23-nt siRNA duplexes by Dicer RNase III and possible other dsRNA-binding factors. The siRNA duplexes are incorporated into a siRNA-containing ribonucleoprotein complex (siRNP) (21) becoming the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) endonuclease, which targets homologous mRNAs for degradation. AGO2 and yet to be characterized proteins are thought to be required for RISC formation. The RISC mediates sequence-specific target RNA degradation. In plants and nematodes, targeted RNAs might also function as templates for double-strand RNA synthesis giving rise to transitive RNAi (24, 80–83), either through siRNA-primed dsRNA synthesis or through unprimed synthesis from aberrant RNA (which could represent the cleaved target RNA). In mammals or in fruitfly, however, RdRP genes have yet been identified, and the major mechanism of siRNA action is believed to be endonucleolytic target RNA cleavage guided by siRNA-protein complexes (RISC).


