
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Molecular Genetics of Human Cognition
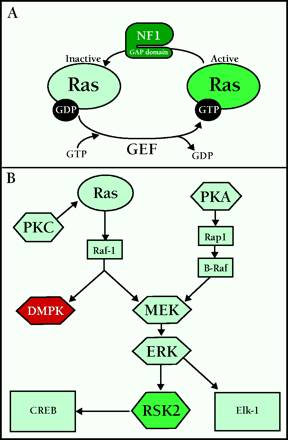
Signaling pathways implicated in human memory formation. A. Ras is a small GTPase whose activity is regulated by the presence of GTP or GDP. When bound to GDP, Ras is inactive. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEF) catalyze the exchange of a molecule of GDP for a molecule of GTP. Once bound to GTP, Ras is activated. GTPase activating proteins (GAP) promote the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP, inactivating Ras. NF1 contains a GAP, and is involved in inactivation of Ras. B. Signaling through PKA and PKC leads to activation of ERK/MAPK. In parallel, Raf-1 also activates the DM1-associated protein kinase (DMPK) involved in myotonic dystrophy. RSK2 is activated by ERK, and regulates gene transcription. CLS is due to disruption of RSK2.


