
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Molecular Genetics of Human Cognition
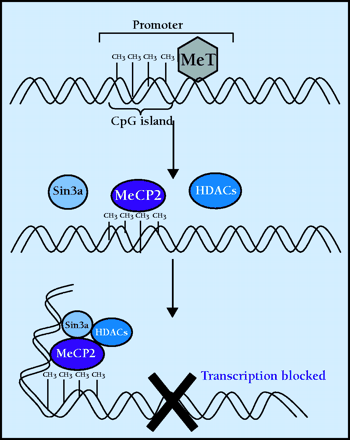
Figure 3.
Repression of transcription via methylation. DNA methyltransferases (MeT) catalyze the methylation of cytosine, producing 5’-methylcytosine (5 mC). Most cytosine methylations occur in cytosine phosphorylated guanine (CpG) dinucleotide repeats (islands). The transcriptional repressor, methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2), binds to 5mCpG and recruits histone deacetylases (HDAC) and corepressors, such as Sin3a. The activity of this protein complex causes a change in chromatin structure such that transcription is blocked. Rett syndrome is believed to be caused by disruption of MeCP2.


