
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Secretory Functions of Smooth Muscle: Cytokines and Growth Factors
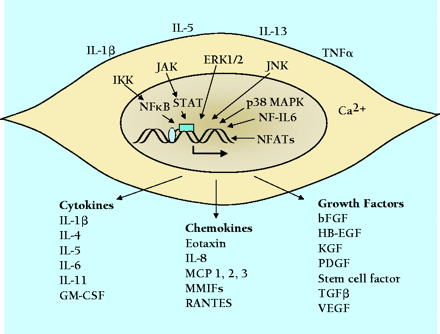
Summary of extracellular stimuli, key signal transduction pathways, and signaling proteins secreted from smooth muscle cells. The extracellular stimuli that appear are examples taken from cell culture studies of vascular, airway, and uterine smooth muscle. IL-1β and TNF-α are the most frequently investigated agents, because they are present at sites of inflammation in the vasculature, the airways, and intestinal tracts. The signal transduction pathways shown are those for which there is evidence in smooth muscle. Many pathways are common to immune cells and are implicated in control of transcription of cytokine and growth factor genes and synthesis of proteins. Each cytokine, chemokine, or growth factor listed has been shown to be synthesized by one or more types of smooth muscle. Some are common to most or all types of smooth muscle, such as IL-1β and bFGF. Others are limited to one particular cell type, such as eotaxin from airway smooth muscle. The functional effects of these agents are varied and in some cases completely different depending on the type of smooth muscle cell.


