
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Galanin in Alzheimer Disease
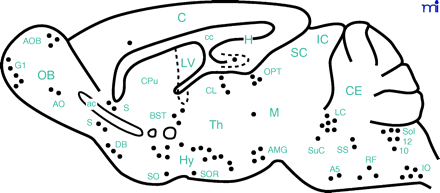
Schematic representation of a sagittal section of the mouse brain showing the distribution of GAL immunoreactivity in neurons (filled circles). A5, A5 noradrenergic cells; ac, anterior commissure; AMG, amygdala; AO, anterior olfactory nucleus; AOB, accessory olfactory bulb; BST, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; C, cerebral cortex; cc, corpus callosum; CE, cerebellum; CL, central lateral thalamic nucleus; CPu, caudate-putamen complex; DB, diagonal band of Broca; G1, glomerular layer of the olfactory bulb; H, hippocampus; Hy, hypothalamus; IC, inferior colliculus; IO, inferior olive; LC, locus coeruleus; LV, lateral ventricle; M, mesencephalic tegment; OB, olfactory bulb; OPT, olivary pretectal nucleus; RF, reticular formation; S, septum; SC, superior colliculus; SO, supraoptic nucleus; Sol, solitary tract nucleus; SOR, retrochiasmatic supraoptic nucleus; SS, superior salivatory nucleus; SuC, subcoreuleus nucleus; Th, thalamus; 10, dorsal motor nucleus of vagus nerve; 12, hypoglossal nucleus.


