
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Protein KINASE C–Dependent Remodeling of Glutamate Transporter Function
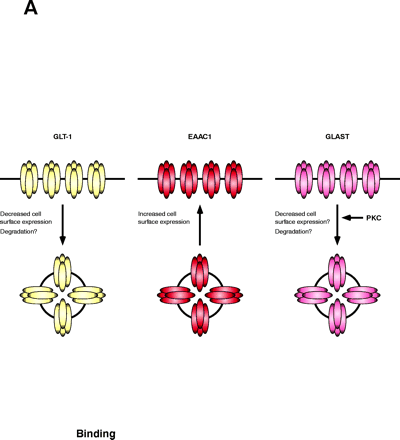
PKC activation differentially regulates the subtypes of glutamate transporters. Activation of PKC causes internalization of the glial glutamate transporter GLT-1, but increases the surface expression of the neuronal transporter EAAC1. One could imagine that simultaneous activation of PKC might provide a mechanism to shift clearance of glutamate from astrocytes to neurons. The activity of GLAST is also regulated by PKC. The specific mechanisms involved in regulation of the glutamate transporters have not been well explored but it is possible that they require the participation of “scaffolding” or “accessory” proteins to increase or reduce the number of active transporters located at the cell surface.


