
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Molecular Targeting in Radiotherapy: Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
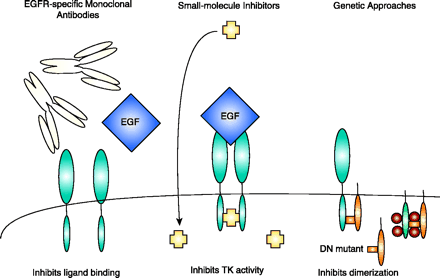
Approaches to disrupting EGFR signaling. At least three approaches are currently studied to target the EGFR. EGFR-specific monoclonal antibodies compete with ligand and behave as receptor antagonists. EGF-specific antibodies are also being used to direct the delivery of radionuclides, toxins, and immunomodulatory molecules. Small-molecule inhibitors interact with the intracellular domain of EGFR and block the TK (tyrosine kinase) activity. Genetic approaches include antisense oligonucleotides to inhibit EGFR expression and overexpression of dominant negative (DN) mutants that form heterodimers with wt EGFR or constitutively activated EGFR.


