
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Few Things in Life are “Free”: Cellular Uptake of Steroid Hormones by an Active Transport Mechanism
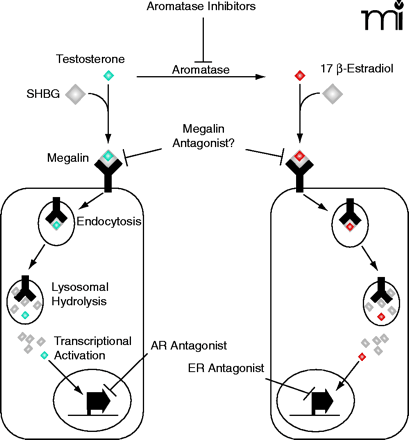
Schematic representation of mechanisms blocking androgen and estrogen actions. Most of the current drugs used to treat steroid-dependent tumors either: 1) block the biosynthesis of steroid hormones (aromatase inhibitors) or 2) prevent transcriptional activation of steroid responsive genes by inhibiting the binding of endogenous steroids to their intracellular receptors (androgen receptor (AR) or estrogen receptor (ER) antagonists). Megalin has been identified as an endocytic receptor for the cellular uptake of steroid/sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) complexes (7). Development of megalin antagonists, that block the entry of steroids into cells, may serve as an alternative or synergistic treatment to presently available therapeutics.


