
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
COX-2 in Inflammation and Resolution
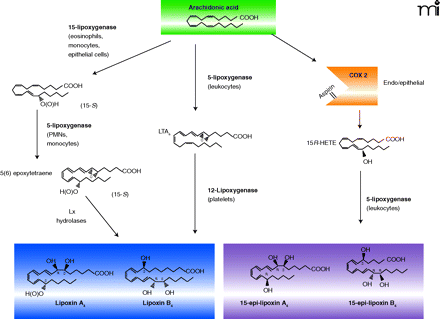
Pathways leading to the production of lipoxins and epilipoxins. I). 15-lipoxygenase produces 15(s)hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid [15S-H(p)ETE], which serves as a substrate for polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) 5-lipoxygenase [5-LOX] to generate 5,6-epoxytetraene. The latter is unstable and is converted to lipoxin A4 and B4 by lipoxin (Lx) hydrolases. II). 5-LOX in PMNs metabloizes arachidonic acid to leukotriene A4 which is taken up by platelets in a transcellular manner and converted by platelet 12-LOX to LxA4. III). Acetylation of the active site of COX-2 by aspirin results in the conversion of arachidonic acid to 15(R)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic [15(R)-HETE] which when released by endothelial and epithelial cells may be transformed by leukocyte 5-LOX to generate 15-epi-LxA4 or 15-epi-LxB4.


