
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Repression of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Transcriptional Activity by Epidermal Growth Factor
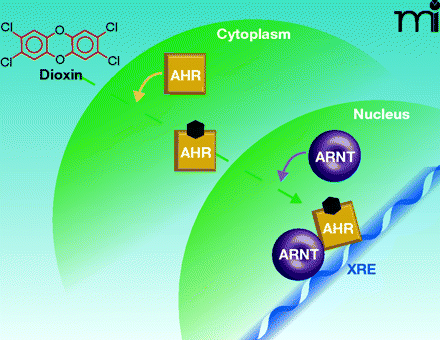
Figure 1.
“Classical” pathway of AHR action. Dioxin (also denoted by the black hexagon) passes into the cytoplasm passively and binds to AHR. AHR translocates into the nucleus where it discards its associated chaperone proteins (not illustrated), dimerizes with ARNT, and binds to XRE sequences in responsive genes.


