|
If the slide opens in your browser, select File -> Save As to save it.)
Copyright restrictions may apply. Please see our Conditions of Use.
Click on image to view larger version.
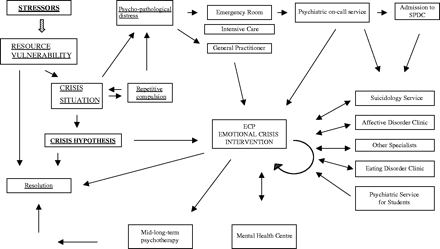
FIGURE 1 Theoretical model of crisis evolution—the part underlined in the top left-hand corner summarizes the theoretical crisis model proposed by Andreoli et al. (1986). Internal or external stressful events may determine a crisis stemming from resource availability and vulnerability of the subject. Although the crisis may be spontaneously resolved, there is a danger of psychopathological degeneration, occasionally through repetitive compulsion and maintenance of the crisis situation, with chiefly egosyntonic characteristics. The crisis hypothesis (which tends to be more egodystonic) marks an opening toward the search for adaptive solutions or treatment and paves the way toward crisis resolution.
Crisis intervention model adopted by Padova Hospital, Italy—the part of the figure that is not underlined represents the crisis model adopted by the ECP in Padova. General Practitioner: referral to the ECP may be directly facilitated by the patient's own family doctor. Psychiatric on-call service: patients going to the emergency room are first assessed by the physician on call who may suggest that the patient make a psychiatric appointment or may contact the psychiatrist on call. The psychiatrist on call may in turn consider referring the patient to the ECP. Suicidology service: the suicidology service has consultants who may be contacted by the emergency room or by other wards at Padova Hospital following an attempted suicide. The consultants may refer the patient to the ECP in association with other interventions deemed appropriate. In some cases, the ECP consults with the suicidology service in relation to patients expressing serious suicidal ideation. Psychiatric service for students: the psychiatric service for students is a service subsidized by the ESU (the Board for the Right to University Study), which provides intervention for those university students requesting it. The ECP is one type of intervention that might be proposed. Affective disorder clinic, Eating disorder clinic, Other specialists, and Mental health center: patients may be referred to the ECP from these specialist clinics or by other specialists when circumstances so demand. Likewise, when patients do not meet inclusion criteria for crisis intervention, the ECP may in turn refer patients to these units. Medium/long-term psychotherapy: in some cases, intervention by the ECP may give rise to a request for medium/long-term therapy. In such cases, the request is assessed, and where appropriate, this solution is recommended.
|