
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
CTLA-4: Acting at the Synapse
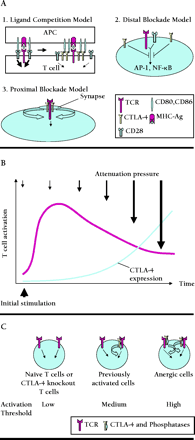
A. Three models for T cell inhibition by CTLA-4. 1. Ligand Competition Model wherein CTLA-4 can successfully compete with CD28 for CD80 and CD86 binding because of CTLA-4’s stronger avidity. 2. Distal Blockade Model wherein CTLA-4 inhibits distal pathways of TCR–CD28 signaling. 3. Proximal Blockade Model wherein CTLA-4 is recruited to the immunological synapse and blocks early signal transduction via the TCR. B. Attenuation model: In single T cells, CTLA-4 is synthesized during the time course of T cell activation and is recruited to the T cell surface. As a consequence, the T cell signal is attenuated and T cell activation is inhibited. C. Threshold model: In the absence of CTLA-4 (naïve cells and CTLA-4 knockout cells), the minimal requirement for T cell activation is very low. However, once CTLA-4 is induced (e.g., in previously activated cells or anergic cells), CTLA-4 is recruited to the immunological synapse where it increases the activation threshold either at the level of antigen specific (TCR) or co-stimulatory (CD28) signals.


