
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Regulation of Gene Expression by the Hypoxia-Inducible Factors
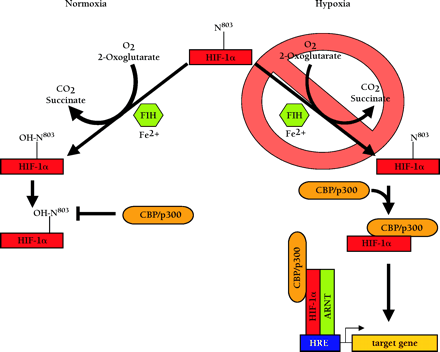
Figure 4.
Oxygen-dependent transcriptional inactivation of HIF-1a and HIF-2a. In normoxia, a specific asparagine within HIF-1α (N803, or N851 in HIF-2α) is hydroxylated by an O2-, 2-oxoglutarate-, and Fe2+-dependent HIF-α asparagine hydroxylase (FIH-1). This inhibits the direct interaction of the C-terminal transactivation domain (CAD) with CBP/p300 and, ultimately, the assembly of the transcriptional coactivator complex. In hypoxia, the required O2 tension for asparaginyl hydroxylase activity is deficient. As a result, CBP/p300 can associate with the unhydroxylated CAD and potentiate transcriptional activtity.


