
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Ghrelin and the Regulation of Food Intake and Energy Balance
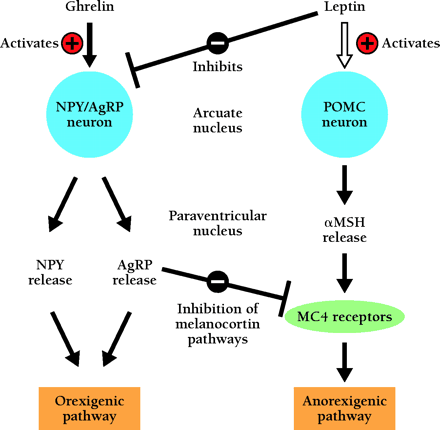
Figure 2.
A simplified model of the feeding-regulatory signaling of ghrelin and leptin. Leptin stimulates the POMC anorexigenic pathway and inhibits the NPY–AGRP orexigenic pathway, resulting in reduced food intake. The effect of ghrelin in the hypothalamus is opposite to that of leptin. The orexigenic effect of ghrelin is mediated by activating on the output of the NPY–AGRP neurons. Fasting increases ghrelin and decreases leptin production, leading to the activation of the orexigenic pathway. This response might be important for the adaptation to fasting.


