
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
LTP May Trigger Addiction
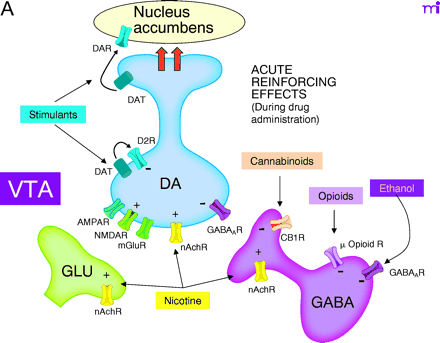
Interactions of reinforcing drugs with the mesoaccumbens dopamine (DA) system, focusing on the ventral tegmental area (VTA). A. Acutely, all reinforcing drugs increase DA transmission in this system. Stimulants (e.g., amphetamine, cocaine) interact with the DA transporter (DAT) to elevate extracellular DA levels, dramatically enhancing DA transmission in nucleus accumbens [but inhibiting DA cell firing through autoreceptors (D2R) in the VTA]. Nicotine, through nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAchR) excites DA cells directly and promotes glutamate release from glutamate nerve terminals (GLU) in the VTA. Opioids, through opioid receptors, inhibit -amino butyric acid (GABA) neurons in the VTA, disinhibiting DA neurons. Actions in the nucleus accumbens are also important for opioid reinforcement. Ethanol and cannabinoids also interact with VTA GABA neurons to disinhibit DA neurons. Ethanol is a positive allosteric modulator of GABA A receptors, whereas cannabinoids activate presynaptic CB1 receptors that inhibit GABA release.


