
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
ROLE of MITOCHONDRIA in TOXIC OXIDATIVE STRESS
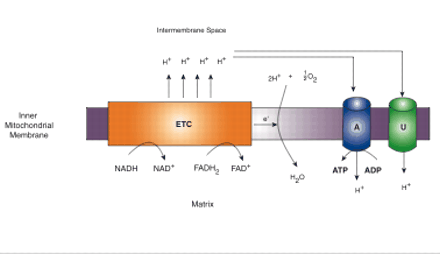
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC) and coupling and uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation. Reduced substrates NADH and FADH2 are oxidized, with electrons passing to the enzyme complexes of the ETC and the protons (H+) pumped into the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion, forming a large mitochondrial membrane potential known as the proton-motive force. Energy lost by protons re-entering the mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase (A) is used to power generation of ATP from ADP. Protons may also re-enter the matrix via uncoupling proteins (U), such as UCP2, without production of ATP.


