
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
HANGING IN THE BALANCE
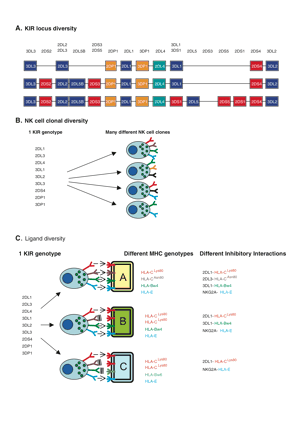
KIR generate diversity at multiple levels. A. The population diversity of KIR. A schematic is shown of the gene content illustrating three of the many possible different KIR haplotypes. Activating genes are in red, inhibitory genes in blue, and pseudogenes are in orange. B. Clonal expression of KIR. Shown are four potential NK cells derived from a single individual. KIR expression is clonal and in this illustration the individual NK cells express different combinations of KIR. C. Diversity in the HLA Class I ligands for KIR generate a functional KIR diversity. Illustrated are the functional effects of different HLA class I types in three individuals with the same KIR genotype. Individual A has four potential KIR:HLA inhibitory interactions, individual B has three, and individual C has two. All individuals have the NKG2A:HLA-E receptor ligand combination which exhibits very limited population diversity. Thus, the number of potential different inhibitory receptor:ligand interactions in each individual is different.


