
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
The Neuronal Death Protein Par-4 Mediates Dopaminergic Synaptic Plasticity
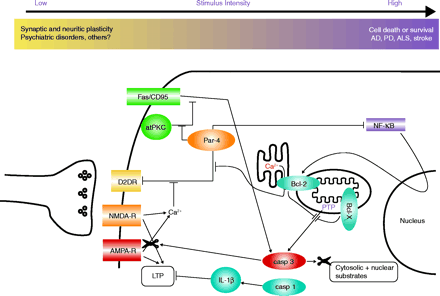
Interactions of apoptosis pathways with calcium signaling and synaptic transmission. Par-4 can transduce classical apoptosis pathways like Fas/CD95-mediated cell death by interaction with atypical PKC (ζ) or by inhibiting NF-κB–mediated expression of Bcl-2. At the same time, Par-4 interacts with the D2 dopamine receptor at synapses to inhibit downstream dopamine signaling. This latter interaction is antagonized by calcium-activated calmodulin. Bcl-2, apart from its most typical action, inhibiting the formation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore, also enhances calcium leakage from the endoplasmic reticulum. Activated caspase-3 can cleave GluR1, an α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionate (AMPA) receptor subunit, thereby modulating intracellular calcium levels. → indicates stimulation and ⊣ indicates inhibition. D2DR, dopamine 2 dopamine receptor; NMDA-R, NMDA receptor; AMPA-R, AMPA receptor, atPKC, atypical PKC (ζ), LTP, long term potentiation; IL-1, interleukin-1β; casp 1, caspase 1; casp 3, caspase 3; PTP, mitochondrial permeability transition pore; NF-κB, Nuclear factor-kappaB; AD, Alzheimer Disease; PD, Parkinson Disease; ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.


