
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
The Pharmocogenomics of Warfarin
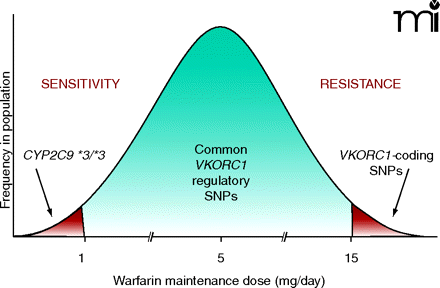
Figure 4.
Genetic liabilities for warfarin sensitivity and resistance. Coding-region mutations in the VKORC1 gene can cause warfarin resistance that necessitates daily doses in excess of 15 mg/day (see also Table 1). Conversely, mutations in the CYP2C9 gene, especially homozygosity for the CYP2C9*3 allele, can result in sensitivity to the drug such that doses less than 1 mg/day are sufficient to achieve therapeutic anticoagulation. Non-coding region polymorphisms in VKORC1 also influence warfarin dose across the “normal” dosing range.


