
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Measuring the Reinforcing Strength of Abused Drugs
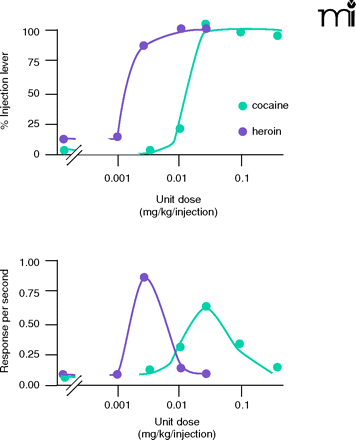
Self-administration by monkeys trained to respond under two concurrent schedules of reinforcement. Monkeys were trained to respond on one lever for food pellets and on an alternate lever for i.v. injections under concurrent FR30;FR30 schedules of reinforcement. The abscissae show the dose per injection. The upper ordinate shows the percentage of responding on the injection-associated lever, whereas the lower ordinate shows the response rate on the injection-associated lever. The availability of i.v. saline (in lieu of drug) results in the allocation of responding to the food-associated lever; the availability of cocaine or heroin results in dose-related increases in the allocation of responding to the injection-lever. In contrast to the monotonic function relating dose to choice (upper panel), response rates first increase and then decrease as a function of dose (bottom panel). Note the similarity between the plots for response rate and for intake (Figure 1).


