
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Microsomal Prostaglandin E2 Synthase: A Safer Target than Cyclooxygenases?
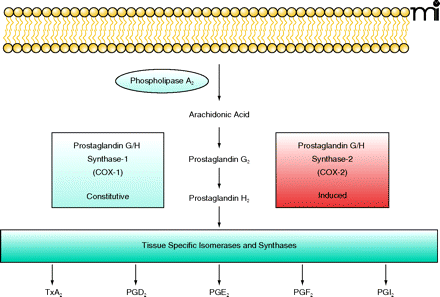
Figure 1.
Prostaglandin biosynthesis pathway. Phospholipase A2 catalyzes the release of arachidonic acid (AA) from the membrane, and AA is converted into prostaglandin G2 and H2 by prostaglandin G/H synthase (PGHS)-1 or -2, which contain both cyclooxygenase activity and hydroperoxidase activity. COX-1 is constitutively expressed in many organs, whereas the expression of COX-2 is inducible. Prostaglandin H2 is further metabolized by tissue specific isomerases and synthases [such as PGE synthases (e.g., microsomal PGE synthase-1) or PGI synthase] to generate diverse prostaglandins. Tx, thromboxane; PG, prostaglandin.


