
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Optimizing Combination Chemotherapy by Controlling Drug Ratios
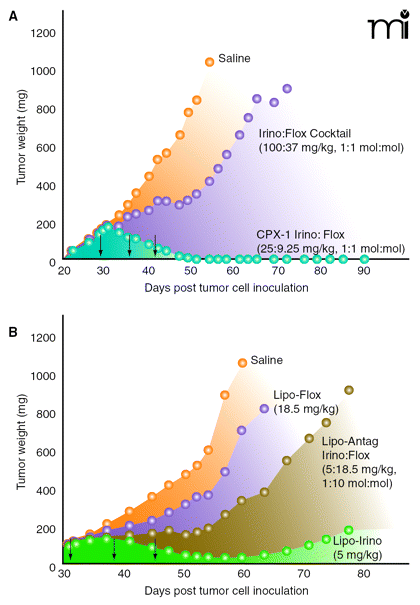
Figure 4.
Increased efficacy of irinotecan and floxuridine depends on delivery of the synergistic ratio. (A) Liposomal delivery of a 1:1 molar ratio of the two drugs (synergistic in vitro) cures mice bearing human pancreatic solid tumors, whereas the conventional cocktail has minimal activity. (B) Liposomal delivery of a 1:10 molar ratio (antagonistic in vitro) is significantly less active against human pancreatic tumors growing in mice; the delivered 1:10 ratio is, in fact, less active than the administration of liposomal irinotecan alone. In both panels, arrows indicate treatment days. See text for details.


