
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Revealing the Potential of Intranasally Administered Orexin A (Hypocretin-1)
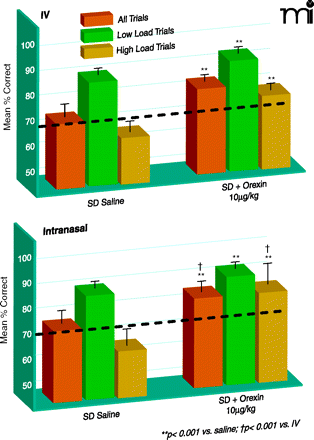
Comparing routes of orexin A administration for efficacy in reversing sleep deprivation deficits. Comparison of the efficacy of intravenous (IV; top panel) and intranasal orexin A (bottom panel) regarding the reversal of sleep deprivation (SD)-induced deterioration of performance in the delayed match to sample (DMS) short-term memory task [from (21)]. Eight adult male rhesus monkeys weighing 8.0–11.0 kg were examined under normal, alert conditions and after 30–36 hours of SD. Effects of the two delivery methods on mean percentage correct (+/−SEM) performance relative to performance levels after SD and saline administration (dotted line) are indicated. Overall performance is shown for all trials (orange bars) and for trials of low cognitive load [green bars; trials with short inter-stimuli delays (1–15 s) and 1–3 distracter images] and high cognitive load [dark gold bars; long duration (60–90 s) trials with 6–8 distracter images]. **p<0.001, difference relative to each respective saline SD condition; †p<0.001, difference between intravenous versus intranasal orexin A in SD condition. Used with permission (22).


