
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Parstatin, a Novel Protease-Activated Receptor 1–Derived Inhibitor of Angiogenesis
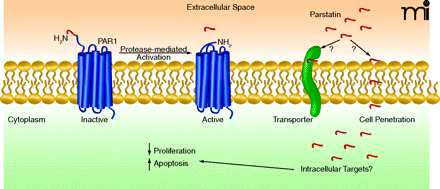
Figure 1
Processing of parstatin from the protease-activated receptor (PAR1). PAR1 is a G protein–coupled receptor expressed on a variety of cell types. Serine proteases activate PAR1 by cleaving a forty-one amino-acid fragment and inducing activation of a tethered ligand. The cleaved peptide, parstatin, localizes at the cell surface and is internalized perhaps by transporter- or lipid-mediated cell penetration. Parstatin subsequently inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis.


