 |
October-December 2011
Volume 5 | Issue 4
Page Nos. 85-107
Online since Tuesday, December 20, 2011
Accessed 18,483 times.
PDF access policy
Full text access is free in HTML pages; however the journal allows PDF access only to users from SOUTH AFRICA and paid subscribers.
EPub access policy
Full text in EPub is free except for the current issue. Access to the latest issue is reserved only for the paid subscribers.
|
| |
|
|
Show all abstracts Show selected abstracts Add to my list |
|
| ORIGINAL ARTICLES |
|
|
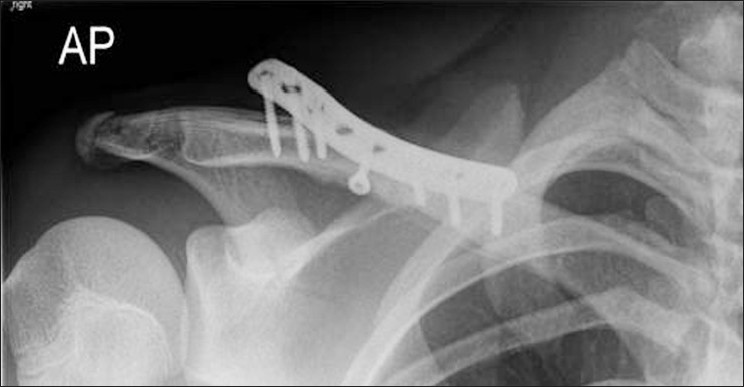  |
Is removal of clavicle plate after fracture union necessary? |
p. 85 |
Janey Wang, Ramiah Chidambaram, Daniel Mok
DOI:10.4103/0973-6042.90998 PMID:22223957Purpose: To review whether clavicle plates should be removed after union of the fracture.
Materials and Methods: 48 patients with middle third clavicle fractures treated by plating were assessed with UCLA shoulder rating and Oxford shoulder scores.
Results: At an average follow up of 13 months,96% of 27 patients with plates out recommended its removal. 86% of 21 patients with plates in were happy to keep them.
Conclusions : We recommend leaving clavicle plates in unless requested by the patient.
Level of Evidence: I V-retrospective study. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (2) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
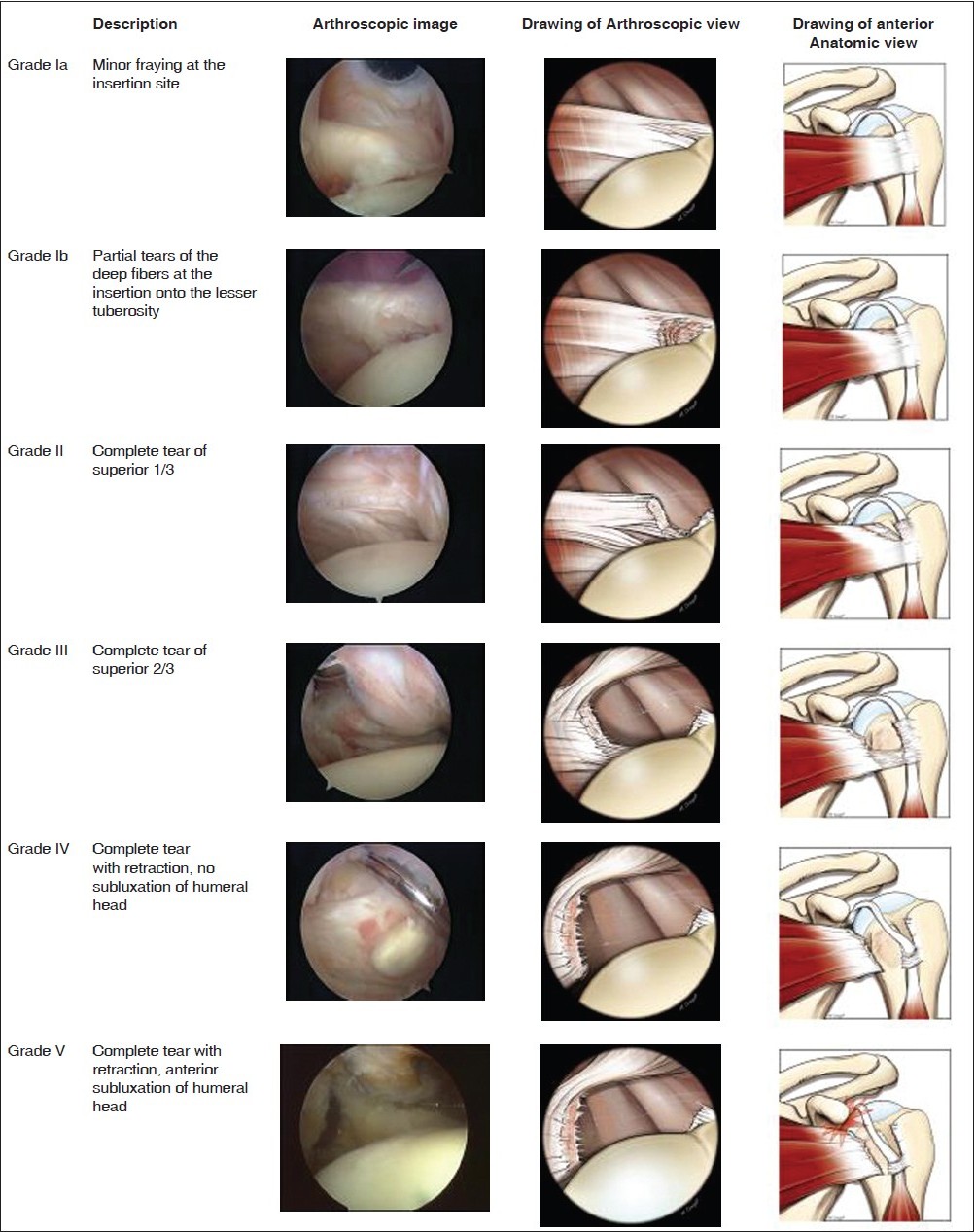  |
The frequency of subscapularis tears in arthroscopic rotator cuff repairs: A retrospective study comparing magnetic resonance imaging and arthroscopic findings |
p. 90 |
Guido Garavaglia, Henri Ufenast, Ettore Taverna
DOI:10.4103/0973-6042.91000 PMID:22223958Purpose: With the advent of arthroscopic shoulder surgery the comprehension and description of rotator cuff tears have strongly evolved. Subscapularis tears are difficult to recognize and are underestimated. Our purpose is to report our observations concerning the relative frequency of subscapularis tears in patients undergoing arthroscopic rotator cuff repair and to compare the arthroscopic observations with the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings.
Materials and Methods: Retrospective cohort study including all patients undergoing arthroscopic rotator cuff repair was performed between March 2006 and March 2009 at our institution. Preoperative MRI findings, intraoperative arthroscopic findings, and details of surgical intervention were collected using medical charts.
Results: We reviewed the medical charts of a total of 348 consecutive arthroscopic rotator cuff repairs. There were 311 supraspinatus tears (89%), 48 infraspinatus tears (14%), and 129 subscapularis tears (37%). MRI sensitivity and specificity were respectively 0.25 and 0.98 for subscapularis tendon tears, 0.67 and 1.0 for supraspinatus tears and 0.5 and 0.99 for infraspinatus tears.
Conclusion: Subscapularis tears are frequent lesions and usually appear concomitantly with supra or infraspinatus lesions. We propose a classification of subscapularis tendon tears, based on our observations of the pathoanatomy of the tears. While concordance with MRI results are good for the supraspinatus, MRI often fails to diagnose the presence of subscapularis tears and infraspinatus tears |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (11) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Latissimus dorsi tendon transfers for rotator cuff deficiency |
p. 95 |
James Donaldson, Adam Pandit, Ali Noorani, Tania Douglas, Mark Falworth, Simon Lambert
DOI:10.4103/0973-6042.91002 PMID:22223959Purpose : Latissimus dorsi tendon transfers are increasingly being used around the shoulder. We aim to assess any improvement in pain and function following a latissimus dorsi tendon transfer for massive, irreparable postero-superior cuff deficiency.
Materials and Methods : At our institution, between 1996 and 2009, 38 latissimus dorsi tendon transfer procedures were performed. Sixteen of these were for massive irreparable rotator cuff deficiency associated with pain and impaired function. All patients were evaluated by means of interview or postal questionnaire and case note review. Pain and function were assessed using the Stanmore percentage of normal shoulder assessment (SPONSA) score, visual analogue scale and Oxford Shoulder Score. Forward elevation was also assessed and a significant improvement was thought to correlate with the success of the procedure at stabilizing the humeral head upon elevation.
Results : Mean follow-up time was 70 months. There was a significant reduction in pain on the visual analogue scale from 6.4 to 3.4 (P < 0.05), an improved SPONSA score from 32.5 to 57.5 (P < 0.05), and an improved Oxford Shoulder Score from 40.75 to 29.6 (P < 0.05). Forward elevation improved from 40° preoperatively to 75° postoperatively (P < 0.05).
Conclusion : Our results add to the body of evidence that latissimus dorsi tendon transfers for irreparable postero-superior cuff deficiency in selected patients reduce pain and improve shoulder function in the medium term.
Level of Evidence : Level 4. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (2) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| CASE REPORT |
 |
|
|
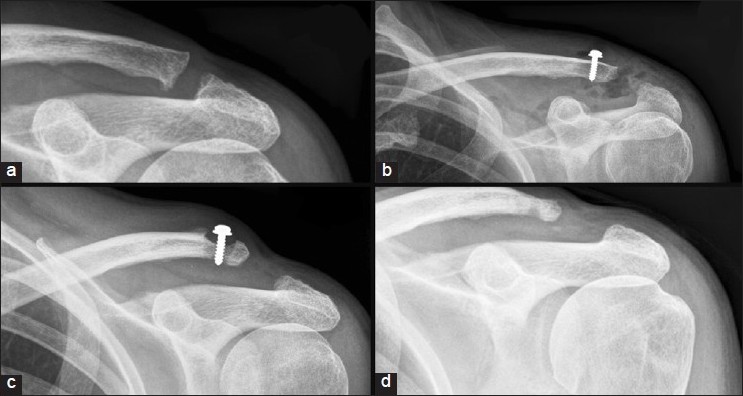  |
Distal clavicle osteolysis following fixation with a synthetic ligament |
p. 101 |
Paul M.C Dearden, Nicholas A Ferran, Emyr W Morris
DOI:10.4103/0973-6042.91003 PMID:22223960We present a case of distal clavicle osteolysis following treatment of a chronic acromioclavicular joint dislocation with a synthetic ligament. The relevant literature is reviewed and discussed. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (2) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| TECHNICAL TIP |
 |
|
|
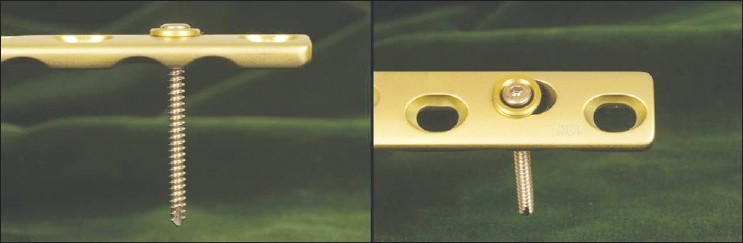  |
Combining of small fragment screws and large fragment plates for open reduction and internal fixation of periprosthetic humeral fractures |
p. 105 |
Dominik Seybold, Mustafa Citak, Matthias Königshausen, Jan Gessmann, Thomas A Schildhauer
DOI:10.4103/0973-6042.91004 PMID:22223961Operative treatment of periprosthetic humeral fractures in elderly patients with osteoporotic bone requires a stable fixations technique. The combination of 3.5 cortical screws with washers in a 4.5 Arbeitsgemeinschaft fόr Osteosynthesefragen, Limited-contact dynamic compression plate or Locking plate, allows a stable periprosthetic fixation with the small 3.5 screws and 4.5 screws above and below the prosthesis, respectively. This combination is a cost-effective technique to treat periprosthetic humeral fractures. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (2) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
