 |
October-December 2015
Volume 9 | Issue 4
Page Nos. 103-144
Online since Thursday, October 22, 2015
Accessed 4,590 times.
PDF access policy
Full text access is free in HTML pages; however the journal allows PDF access only to users from SOUTH AFRICA and paid subscribers.
EPub access policy
Full text in EPub is free except for the current issue. Access to the latest issue is reserved only for the paid subscribers.
|
| |
|
|
Show all abstracts Show selected abstracts Add to my list |
|
| ORIGINAL ARTICLES |
|
|
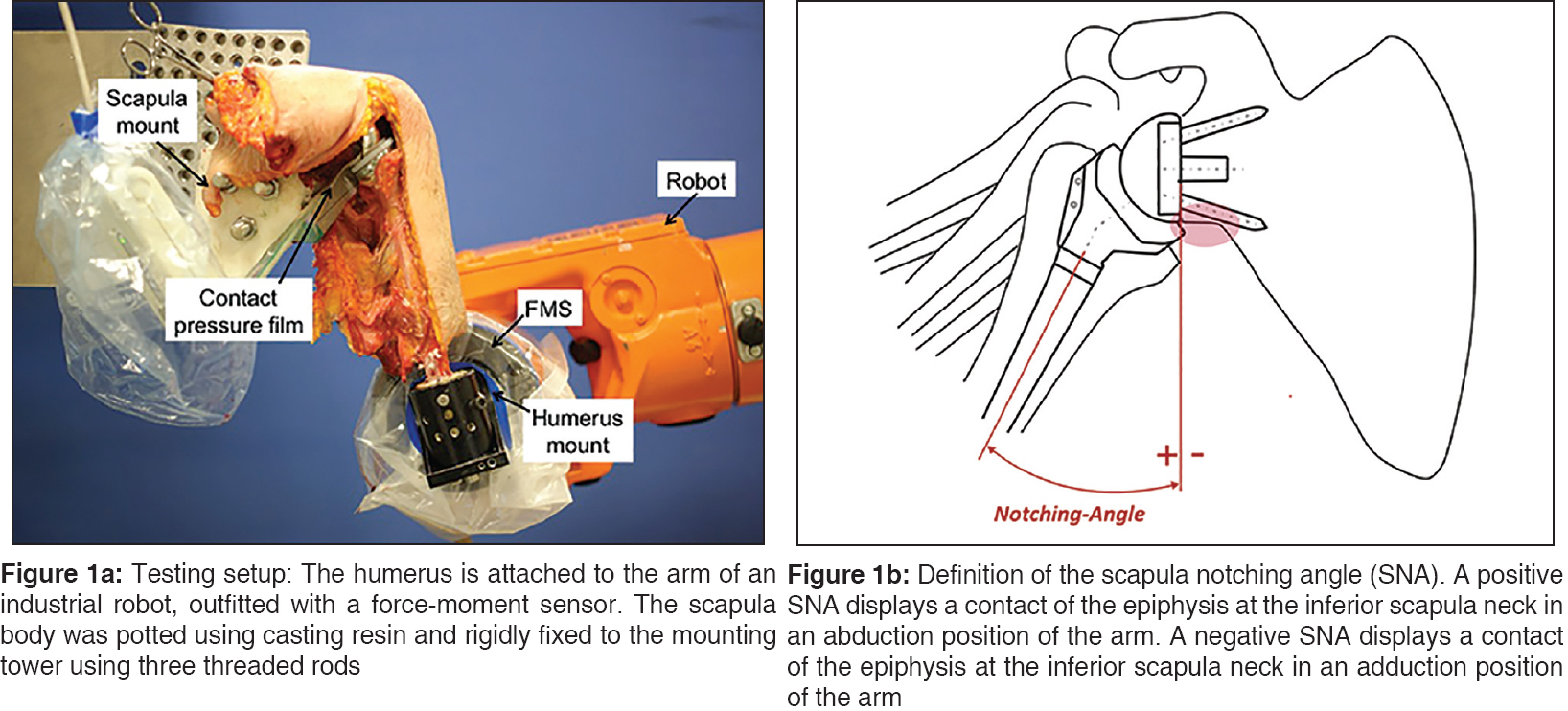  |
Biomechanical evaluation of inferior scapula notching of reverse shoulder arthroplasty depending on implant configuration and scapula neck anatomy |
p. 103 |
Tomas Smith, Alexandra Bäunker, Manuel Krämer, Christof Hurschler, Melena Kaufmann, Marc Frederic Pastor, Mathias Wellmann
DOI:10.4103/0973-6042.167932 PMID:26622125Purpose: The presence of inferior scapula notching is significantly affected by the anatomy the scapula and can be influenced by the glenosphere design and position and the onlay type.
Materials and Methods: A biomechanical study was undertaken with 13 human shoulder specimens in a robot-assisted shoulder simulator. Inferior scapula contact during adduction of the humerus was detected using a contact pressure film. Computed tomography scans with three-dimensional reconstructions of each specimen were performed.
Results: The greatest improvement of the scapula notching angle (SNA) was achieved by simultaneous implantation of a shallow humeral onlay and an eccentric glenosphere design: 16.3-19.0° (P < 0.005). The SNA was significantly decreased by 5.8° when shifting from a 38 mm centric glenosphere to a 42 mm centric glenosphere (P < 0.005) and by 8.9° comparing the 38 mm centric glenosphere with 38 mm eccentric glenosphere (P < 0.005). The solitary implantation of a shallow onlay significantly decreased the SNA depending on the glenosphere size between 7.4° and 8.0° (P = 0.001). A more inferior position of the metaglene as well as a long scapula neck (P = 0.029) and a large lateral scapula pillar angle (P = 0.033) were correlated with a lower SNA.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates the importance of inferior glenosphere placement and the benefit of eccentric glenosphere and shallow humeral cup design to reduce the adduction deficit of the reverse shoulder. The presence of a short neck of the scapula can have a negative prognostic effect on inferior impingement during adduction of the arm.
Level of Evidence: Basic Science Study |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
In-hospital mortality risk for total shoulder arthroplasty: A comprehensive review of the medicare database from 2005 to 2011 |
p. 110 |
Frank McCormick, Benedict U Nwachukwu, Emmanouil B. S. Kiriakopoulos, William W Schairer, Matthew T Provencher, Jonathan Levy
DOI:10.4103/0973-6042.167938 PMID:26622126Introduction: The in-hospital mortality rate after total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) is unknown. The purpose of this study is to quantify the in-patient mortality rates and associated demographic risk factors for patients undergoing a TSA from 2005 to 2011 using a comprehensive Medicare registry database.
Materials and Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of the Medicare database within the PearlDiver database. The PearlDiver database is a publicly available Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act-compliant national database that captures 100% of the Medicare hospital data for TSA between 2005 and 2011. Using International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision codes for TSA we identified a dataset of patients undergoing TSA as well as a subset of those for whom there was a death discharge (i.e., in-patient death). Risk for this outcome was further quantified by age, gender and year. Linear regression was performed to identify risk factors for the primary outcome.
Results: A total of 101,323 patients underwent 125,813 TSAs between 2005 and 2011. There were 113 in-patient mortalities during this period. Thus the incidence of death was 0.09%. Increasing age was a significant risk factor for mortality (P = 0.03). Gender and year of procedure were not significant risk factors for mortality.
Conclusion: The incidence of in-patient mortality for Medicare patients undergoing TSA between 2005 and 2011 was <1 in 1000 surgeries. Increased age is a significant predictor of mortality.
Level 4: Retrospective analysis |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
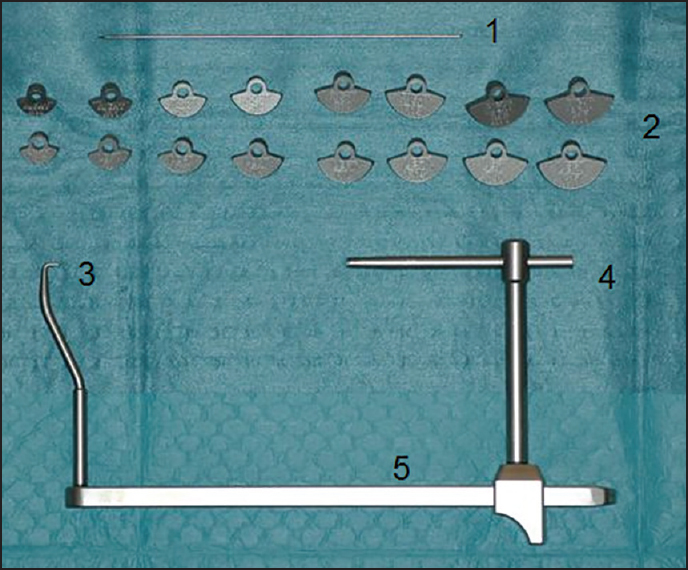  |
Can an extracorporeal glenoid aiming device be used to optimize the position of the glenoid component in total shoulder arthroplasty? |
p. 114 |
Tom R. G. M. Verstraeten, Bart Berghs, Alexander Van Tongel, David Volders, Lieven F De Wilde
DOI:10.4103/0973-6042.167951 PMID:26622127Purpose: Successful total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) requires a correct position of the glenoid component. This study compares the accuracy of the positioning with a new developed glenoid aiming device and virtual three-dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT) scan positioning.
Materials and Methods: On 39 scapulas from cadavers, a K-wire (KDev) was positioned using the glenoid aiming device. It consists of glenoid components connected to the aiming device, which cover 150° of the inferior glenoid circle, has a fixed version and inclination and is available with several different radii. The aiming device is stabilized at the most medial scapular point. The K-wire is drilled from the center of the glenoid component to this most medial point. All scapulas were also scanned with CT and 3D reconstructed. A virtual K-wire (Kct) was positioned in the center of the glenoid and in the scapular plane. Several parameters were compared. Radius of the chosen glenoid component (rDev) and the virtual radius of the glenoid circle (rCT), spinal scapular length with the device (SSLdev) and virtual (SSLct), version and inclination between KDev and Kct, difference between entry point and exit point ("Matsen"-point).
Results: Mean rDev: 14 mm ± 1.7 mm and mean rCT: 13.5 mm ± 1.6 mm. There was no significant difference between SSLdev (110.6 mm ± 7.5 mm) and SSLct (108 mm ± 7.5 mm). The version of KDev and Kct was −2.53° and −2.17° and the inclination 111.29° and 111.66°, respectively. The distance between the "Matsen-point" device and CT was 1.8 mm.
Conclusion: This glenoid aiming device can position the K-wire on the glenoid with great accuracy and can, therefore, be helpful to position the glenoid component in TSA. The level of evidence: II.
|
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
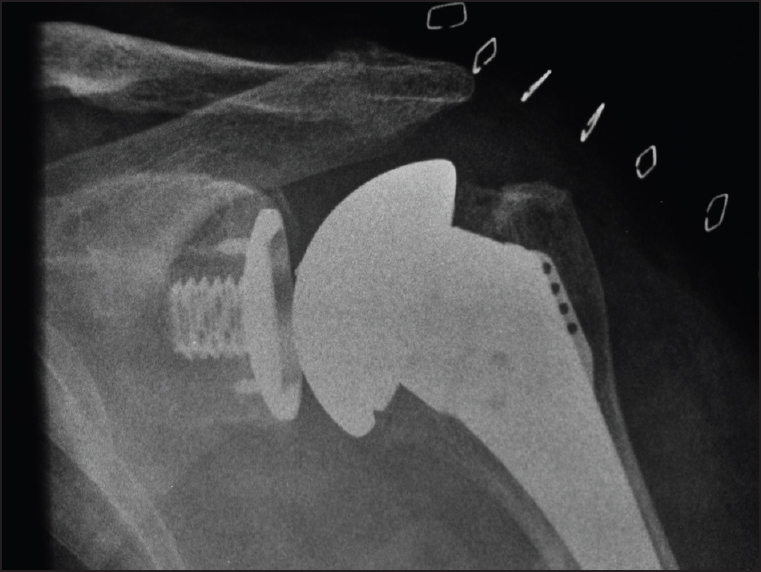  |
Catastrophic failure of a low profile metal-backed glenoid component after total shoulder arthroplasty |
p. 121 |
Carley B Vuillermin, Mark E Trump, Shane A Barwood, Gregory A Hoy
DOI:10.4103/0973-6042.167952 PMID:26622128Context: The longevity of the glenoid component in total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) continues to be problematic. All polyethylene glenoid components have been most widely used, but loosening rates with time and the need for revision has resulted in high-profile metal-backed components with the potential for a more stable prosthesis bone interface and liner exchange. High revision rates in the high profile metal backed designs led us to evaluate a low profile metal backed component.
Aims: To examine the rate and mode of failure of a TSA in a single surgeon consecutive series that has been identified by the Australian National Joint Replacement Registry to have a higher than anticipated rate of revision.
Materials and Methods: This is a single surgeon retrospective consecutive series of 51 arthroplasties undertaken in 50 patients (18 males and 32 females) with an average age of 70.4 ears (range 51-90) and mean follow-up of 5.5 years (range 3.7-8.1).
Results: We observed a very high (29%) rate of revision of the metal-backed glenoid components in this series. The primary mode of failure was glenoid baseplate nonintegration which with a well-fixed central cage screw led to bone resorption and implant breakage or disassembly.
Conclusion: Analysis of the mode of failure of implants identified by robust registries is essential for the development of new prostheses and the pursuit of prosthesis longevity. This low profile metal backed prosthesis has been withdrawn, but without a published mechanism of failure. We feel that any prosthesis withdrawal should be accompanied by appropriate published mechanisms to prevent future component design errors based on similar design problems. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| CASE REPORTS |
 |
|
|
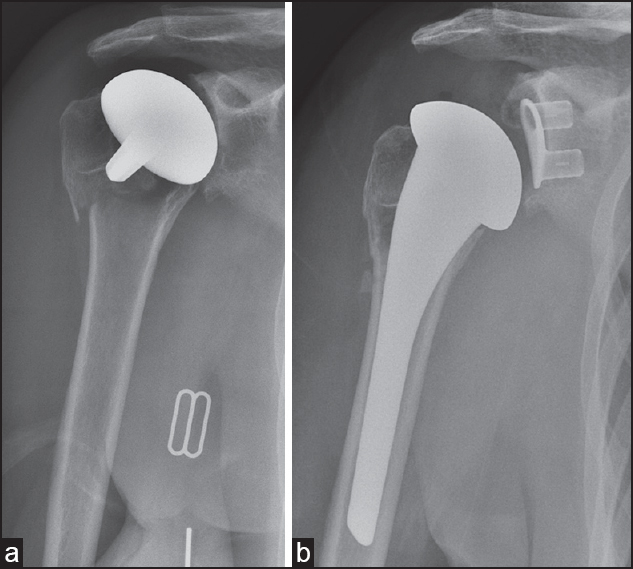  |
Periprosthetic humeral fracture after Copeland resurfacing and the role of revision arthroplasty: A report of three cases |
p. 128 |
Simon Bruce Murdoch MacLean, Karanjit Mangat, Rajpal Nandra, Socrates Kalogrianitis
DOI:10.4103/0973-6042.167953 PMID:26622129Follow-up series of the Copeland resurfacing hemiarthroplasty have reported few postoperative fractures around the prosthesis. We report three cases of periprosthetic fracture around a Copeland resurfacing arthroplasty. Due to prosthetic loosening and tuberosity comminution, all cases were managed with revision shoulder arthroplasty. All patients had good functional outcome and range of movement on early follow-up. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
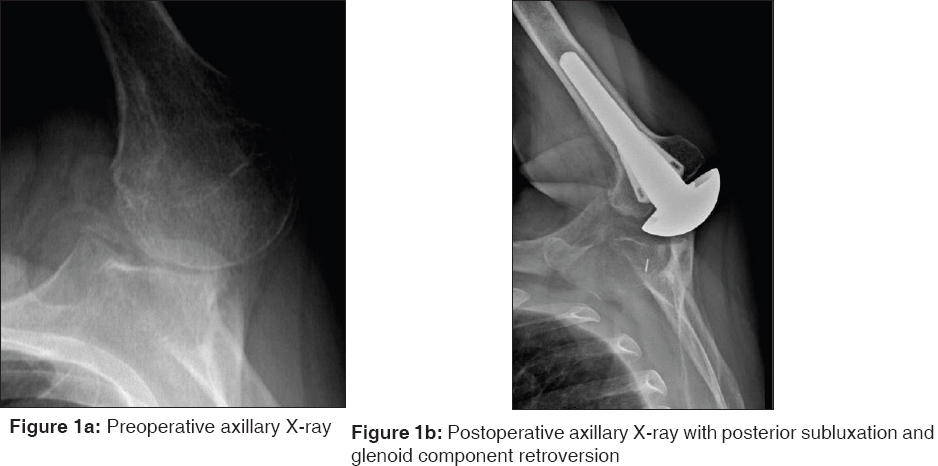  |
Posterior shoulder instability following anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty: A case report and review of management |
p. 131 |
Joseph W Galvin, Josef K Eichinger, Robert E Boykin, Gregor Szöllösy, Laurent Lafosse
DOI:10.4103/0973-6042.167955 PMID:26622130We report a case of posterior shoulder instability following anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA). In addition, we present guidelines to aid in the management of posterior instability after TSA. A 50-year-old male underwent anatomic TSA for glenohumeral osteoarthritis. Postoperatively, the patient developed posterior instability secondary to glenoid retroversion. He did not improve despite conservative treatment. He underwent an arthroscopic posterior bone block procedure, 4-month after his index arthroplasty. At 14-month follow-up, the patient had regained near full motion and strength, and radiographs demonstrated osseous integration with no evidence of component loosening. Posterior instability following TSA is a relatively rare complication and challenging to manage. The posterior, arthroscopic iliac crest bone block grafting procedure represents a treatment option for posterior instability in the setting of a stable glenoid prosthesis following TSA.
|
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
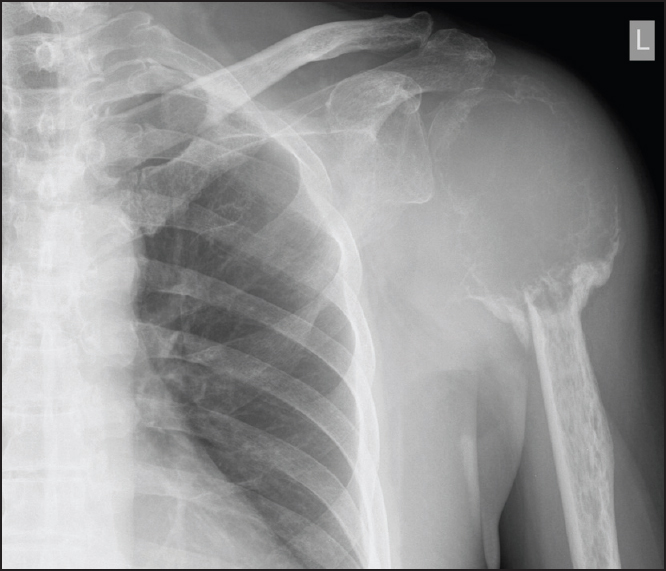  |
Giant cell tumor of the humeral head treated by denosumab: Implication to shoulder surgeons |
p. 135 |
Ka Hei Leung, Albert Ying Lee Lam, Kenneth Wai Yip Ho, Tony Wai Hung Shek
DOI:10.4103/0973-6042.167956 PMID:26622131Giant cell tumor is a benign bone tumor that is commonly encountered. The optimal treatment of a giant cell tumor which causes extensive bony destruction is controversial. Recent studies on the receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand antagonist denosumab may offer a new treatment option for these patients. We presented a patient with giant cell tumor of the humeral head. He was initially treated with denosumab and subsequently with the operation. The shoulder joint was successfully salvaged. But there are potential difficulties that surgeons may face in patients treated with denosumab. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| REVIEW ARTICLE |
 |
|
|
  |
Propionibacterium acnes infection after shoulder surgery |
p. 139 |
Benjamin K Kadler, Saurabh S Mehta, Lennard Funk
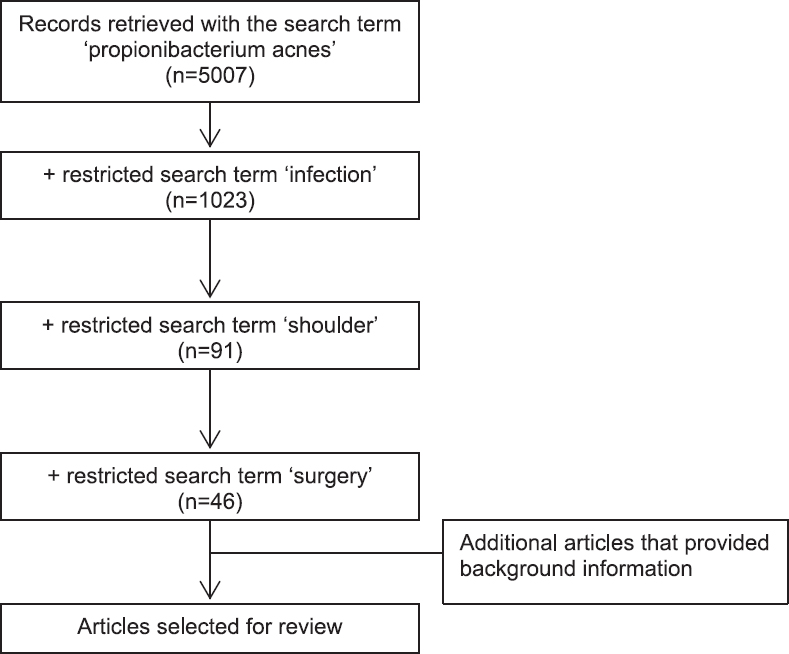
DOI:10.4103/0973-6042.167957 PMID:26622132Propionibacterium acnes has been implicated as a cause of infection following shoulder surgery, may occur up to 2 years after the index operation and has been shown to be responsible for up to 56% of shoulder infections after orthopedic implant. Male patients within the population undergoing shoulder surgery are particularly at risk, especially if their shoulder surgery involved prosthesis or was posttraumatic. P. acnes infection can be difficult to diagnose clinically and laboratory techniques require prolonged and specialized cultures. Usual inflammatory markers are not raised in infection with this low virulence organism. Delayed diagnosis with P. acnes infection can result in significant morbidity prior to prosthesis failure. Early diagnosis of P. acnes infection and appropriate treatment can improve clinical outcomes. It is important to be aware of P. acnes infection in shoulder surgery, to evaluate risk factors, to recognize the signs of P. acnes infection, and to promptly initiate treatment. The signs and symptoms of P. acnes infection are described and discussed. Data were collected from PubMed™ , Web of Science, and the NICE Evidence Healthcare Databases - AMED (Ovid), BNI (Ovid), CINAHL (EBSCO), Embase (Ovid), HMIC: DH-Data and Kings Fund (Ovid), Medline (Ovid), and PsycINFO (Ovid). The search terms used were "P. acnes," "infection," "shoulder," and "surgery." In this review, we summarize the current understanding of the prevention and management of P. acnes infection following shoulder surgery. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
