|
Show all abstracts Show selected abstracts Add to my list |
|
| REVIEW ARTICLE |
|
|
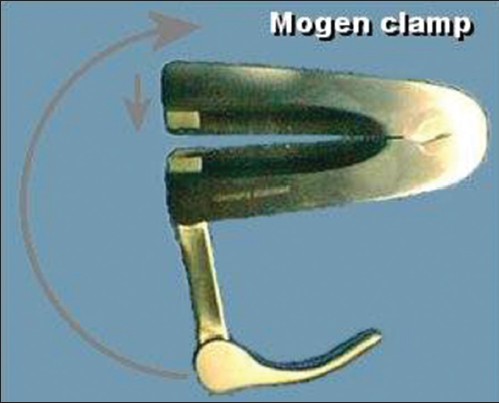  |
Techniques of male circumcision  |
p. 1 |
Abdullahi Abdulwahab-Ahmed, Ismaila A Mungadi
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118588 PMID:24470842Male circumcision is a controversial subject in surgical practice. There are, however, clear surgical indications of this procedure. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends newborn male circumcision for its preventive and public health benefits that has been shown to outweigh the risks of newborn male circumcision. Many surgical techniques have been reported. The present review discusses some of these techniques with their merits and drawbacks. This is an attempt to inform the reader on surgical aspects of male circumcision aiding in making appropriate choice of a technique to offer patients. Pubmed search was done with the keywords: Circumcision, technique, complications, and history. Relevant articles on techniques of circumcision were selected for the review. Various methods of circumcision including several devices are in use for male circumcision. These methods can be grouped into three: Shield and clamp, dorsal slit, and excision. The device methods appear favored in the pediatric circumcision while the risk of complications increases with increasing age of the patient at surgery. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ORIGINAL ARTICLES |
 |
|
|
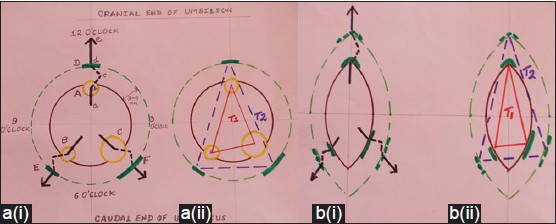  |
Trans-umbilical laparoscopic appendectomy for acute appendicitis without raising skin-flaps: An easy-to-use modification applied to the series of 164 patients from a rural institute of central India |
p. 8 |
Priyadarshan Anand Jategaonkar, Sudeep Pradeep Yadav
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118593 PMID:24470843Background: Laparoscopic appendectomy (LA) is widely used and generally an accepted method for managing appendicitis. And the recent invention of laparoscopic trans-umbilical-appendectomy is a further improvement
of LA. However, it requires expensive instruments with the requisite expertise. We discuss a useful modification of trans-umbilical appendectomy for acute appendicitis using routine instruments. Materials and Methods: From
August 2009 to March 2011, 164 patients were operated by this method at our rural center. Out of them, 102 were males and 62, females. Mean age for males was 27.5 years (range, 14-51) and females, 31.2 years (range, 17-48). Mean body mass index was 21.7 kg/m2 (range, 16.2-29) and 23.2 kg/m2 (range, 17.4-30) for males and females respectively. Acute appendicitis patients wherein surgery was deemed essential were offered this technique. Three umbilical ports (one 10 mm and two 5 mm) were strategically placed to dissect out appendix. Routine laparoscopic instruments were used for all. Results: Mean operativetime was 45 min (range, 30-90) with 1.8% conversion-rate to conventional laparoscopy. Average blood-loss was 15 ml (range, 10-25). We had one caecal electrosurgical injury, which was managed expectantly. Umbilical sepsis and seroma were 3% and 6.1% respectively. Patients were discharged after an average 1.3 days (range, 1-4). The scars had receded in the umbilicus giving a near-scarless abdomen. Discussion: Recently developed technique of single-port appendectomy has primarily been used for chronic appendicitis. Moreover, >1 inch incision inducted per-umbilicum rises the attendant morbidity. We study a surgeon-friendly simple technique applied to acute appendicitis. Conclusion: Method described here is feasible
and safe for managing acute appendicitis. It can be learnt rather easily (learning curve of 15 cases) by a laparoscopic surgeon and avoids expensive instrumentation. Thus, it may stand out in providing benefits of modern surgery to population of developing countries. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
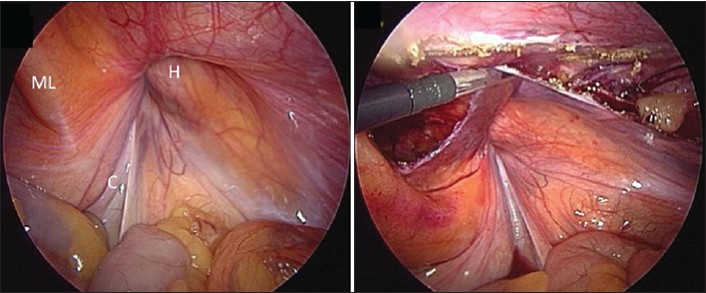  |
Laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair in a developing nation: Short-term outcomes in 103 consecutive procedures |
p. 13 |
Shamir O Cawich, Sanjib K Mohanty, Kimon O Bonadie, Lindberg K Simpson, Peter B Johnson, Sundeep Shah, Eric W Williams
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118601 PMID:24470844Background: There are no published data on the outcomes of inguinal hernia repair from the Anglophone Caribbean. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of a series of laparoscopic inguinal hernia repairs from the region. Materials and Methods: Data was extracted from a prospectively maintained database of consecutive trans abdominal pre-peritoneal (TAPP) repairs done between June 1, 2005 and May 30, 2012. Perioperative data collected included patient demographics, hernia type, operative technique, duration of surgery, intra-operative details, morbidity, analgesia requirements, and duration of hospitalization. A telephone survey was also performed to identify late recurrences and complications. Descriptive statistics were generated using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) Ver 12.0. Results: There were 103 consecutive TAPP procedures in 88 patients at an average age of 35.4 years ± 12.9 (standard deviation; SD) and average body mass index (BMI) of 28.9 Kg/m 2 ± 2.23 (SD). The indications were bilateral (30), recurrent unilateral (24), and primary unilateral (49) inguinal hernias. The mean duration of operation was 68.5 minutes (SD ± 10.4; Range: 55-95; Median 65; Mode 65) minutes for unilateral TAPP and 89 minutes (SD ± 7.61; Range: 80-105; Median 90; Mode 90) for bilateral repairs. Post-operatively, 65/70 patients required ≤1 dose of parenteral opioid analgesia and 74 (84.1%) patients discontinued oral analgesia within 48 hours of operation. Complications were recorded in six (5.8%) cases and a recurrence in one (0.97%) case after a mean follow-up period of 3.2 years (SD ± 1.8; Range: 0.5-7). Conclusion: Laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair is a safe and effective operation in this setting. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (1) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SURGICAL TECHNIQUES |
 |
|
|
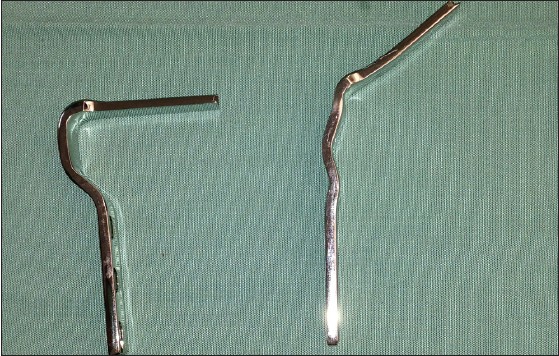  |
A simple technique for adjustment of the femoral offset at the site of hip spacer implantation |
p. 18 |
Konstantinos Anagnostakos, Olaf Lorbach, Patrick Orth, Katrin Koch
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118605 PMID:24470845The decrease of femoral offset might play a role in the emergence of hip spacer dislocations, but it has not been discussed in the literature yet. The present work describes a technique for femoral offset adjustment. Either a bended blade plate or a dynamic hip screw can be used. The depth of the insertion and the angle of the particular implant are defined by the size of the offset adjustment required in each case. The described technique is feasible to produce a customized hip spacer, allowing for the preservation of an adequate muscle tension by individual adjustment of the femoral offset between stages. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| CASE REPORTS |
 |
|
|
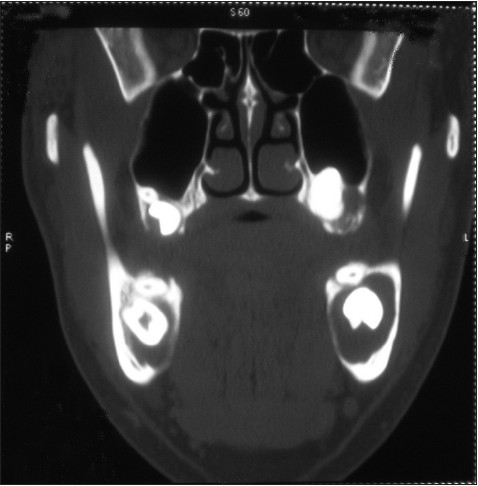  |
Dentigerous cysts in four quadrants: A rare and first reported case |
p. 21 |
Vinit Aher, Prasant Mohan Chander, Rajkumar Garudanahally Chikkalingaiah, Fareedi Mukram Ali
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118607 PMID:24470846The dentigerous cyst is a developmental odontogenic cyst which usually occurs in the second and third decade of life. Dentigerous cyst is one of the most prevalent types of odontogenic cysts associated with partially erupted, developing, or impacted teeth. The mandibular third molars have a high predictability followed by maxillary canines. Occurrence of dentigerous cyst bilaterally is generally observed in syndromic cases. Non-syndromic dentigerous cyst occurring bilaterally or involving both arches at the same time is very rare. This presented case is rare and unique in which all four quadrants shows the presence of dentigerous cyst. In this case there are well-defined cysts associated with impacted molars as well as with supernumerary teeth in all the four quadrants of jaws. The clinical documentation of such a case in available literature is found to be first time. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (3) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
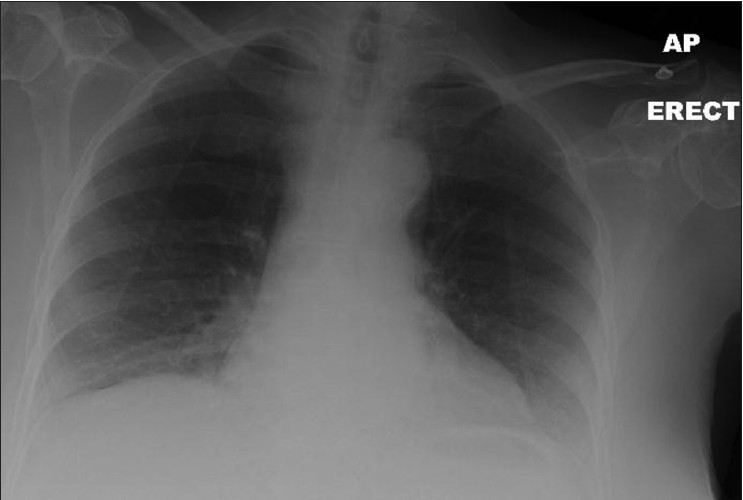  |
Pneumobilia: A case report and literature review on its surgical approaches |
p. 27 |
Chee Siong Wong, James Maurice Crotty, Syed Altaf Naqvi
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118616 PMID:24470847Gallstones ileus is an uncommon cause but important cause of small bowel obstruction. The gallstone enters the intestinal lumen via a fistula located in the duodenum (cholecystoduodenal), or rarely, in the colon (cholecystocolonic) or stomach (cholecystogastric). This may result in large bowel or gastric outlet obstruction (Bouveret's Syndrome). Gallstone ileus affects the elderly females pre-dominantly and is associated with a high morbidity and mortality rate if diagnosis and urgent surgical intervention are delayed. In this paper, we report on the case of an elderly lady who presented with classical symptoms and signs of small bowel obstruction. She was subsequently diagnosed with gallstone ileus due to a large gallstones lodged in the intestinal lumen. We perform a literature review on this rare disease and discuss the two main surgical approaches in managing this condition. Gallstone ileus should be considered in the differential diagnosis of small bowel obstruction especially in elderly women who have no history of abdominal surgery or abdominal hernia. Early intervention is important because of the high mortality rate due to the poor general condition that often exists in this subgroup of patients. There is no general consensus on gold standard surgical approach in these cases but a two-stage procedure (either enterotomy alone or enterotomy and subsequent cholecystectomy) has been shown to be associated with lower mortality rates. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
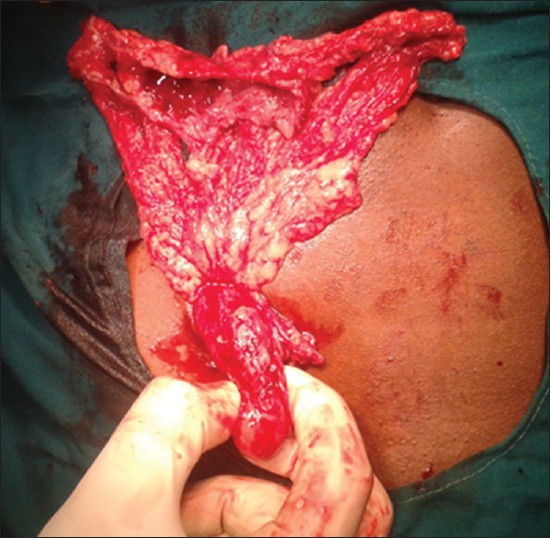  |
Primary tuberculosis of the appendix: A rare cause of a common disease |
p. 32 |
BJ Sharath Chandra, TU Girish, PB Thrishuli, HG Vinay
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118619 PMID:24470848Tuberculosis is still a common infection in India. Although the ileocecal region is the most affected part in intestinal tuberculosis, acute tuberculous appendicitis is quite a rare entity. Our case report highlights a rare presentation of tuberculosis and a brief review of literature. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
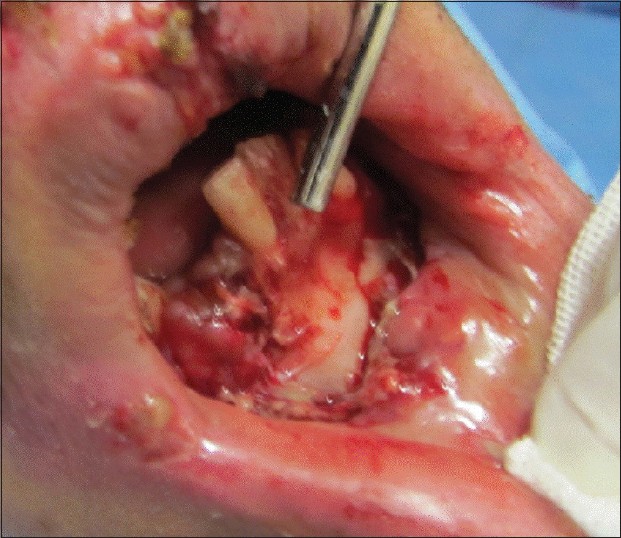  |
Bone suture in management of mandibular degloving injury |
p. 35 |
Amin Rahpeyma, Saeedeh Khajeahmadi
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118622 PMID:24470849Traumatic degloving injuries of the mandible are rare intraoral soft tissue traumas. A simple review of the medical literature shows that no article up to this date has reported the prevalence of the degloving injuries of the mandible. Moreover, the highest incidence of mandibular degloving injuries is reported in children and young adults. In this article, the author describes the mandibular degloving injury, characterized by the separation of periosteum and soft tissues of the anterior buccal side of the mandible, and the bone suture technique. This article outlines that a correct diagnostic assessment and appropriate treatment plan can reduce the complications after mandibular degloving injuries. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (1) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
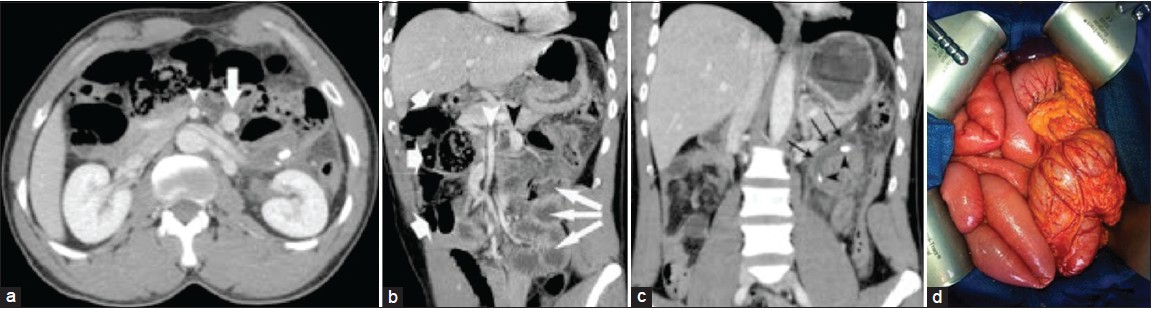  |
Left side appendicitis with midgut malrotation in an adult |
p. 38 |
David Jérémie Birnbaum, Yann Geffroy, Géraldine Goin, Paul Balandraud
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118627 PMID:24470850Midgut malrotation (MMR) is a congenital anomaly referring to either nonrotation or incomplete rotation of the primitive intestinal loop around the axis of the superior mesenteric artery during fetal development. Adult MMR is rare and majority of MMR in adults remains asymptomatic throughout life. The increasing use of diagnostic imaging for acute abdominal pain will lead to more incidental recognitions of MMR. Up to now, surgical treatment has been guided by the experience from pediatric surgery, and Ladd's procedure has been the treatment of choice in adults with MMR. However, a major dilemma arises when patients are essentially asymptomatic and incidentally diagnosed with MMR during another abdominal affection like acute appendicitis. The surgeon has to decide whether it is necessary to also treat the MMR. Here, we report a rare case of a 37-year-old patient with acute left side appendicitis in association with asymptomatic MMR. We discuss whether correction of the asymptomatic malrotation was indicated. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
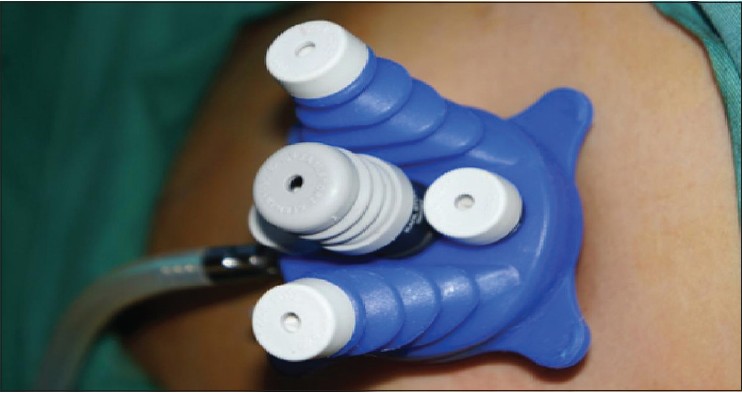  |
Single incision laparoscopic surgery for a large endometriotic cyst |
p. 41 |
Ying Woo Ng, Catherina Josephine Goenadi, Yoke Fai Fong
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118628 PMID:24470851We describe a technique for the treatment of large benign ovarian cysts by single port laparoscopic surgery via the umbilical approach. X-cone single port system (Karl Storz) was employed in this surgery. Prebent atraumatic grasping forceps were used in conjunction with the straight laparoscopic instruments. We propose using a "to-fro" peeling technique in the z-axis in SPLS cystectomy. Combined use of prebent and straight laparoscopic instruments enables the cystectomy to be performed in the z-axis, thereby avoiding instruments crossing and hands collision outside the abdomen. The proposed technique proved to be feasible, easy to employ, and safe in SPLS cystectomy, with the additional benefi t of superior cosmetic outcome. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (1) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
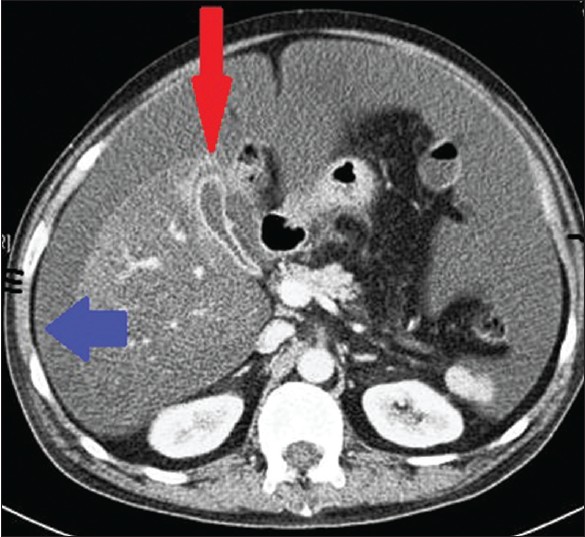  |
Non-operative management of gallbladder perforation after blunt abdominal trauma |
p. 45 |
Rohan Kumar
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118629 PMID:24470852Isolated gallbladder perforations following blunt abdominal trauma are very rare. They often present with insidious onset of symptoms a few days after the initial insult and an operative course of management ensues. This is in the form of a cholecystectomy and peritoneal lavage; more often via laparotomy rather than laparoscopically. Conservative management, in the form of cholecystostomy, percutaneous intraperitoneal drainage or cholecystorraphy has been described; however, these cases have invariably resulted in cholecystectomy eventually. The case uniquely highlights the successful non-operative management of isolated traumatic gallbladder perforation. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (1) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
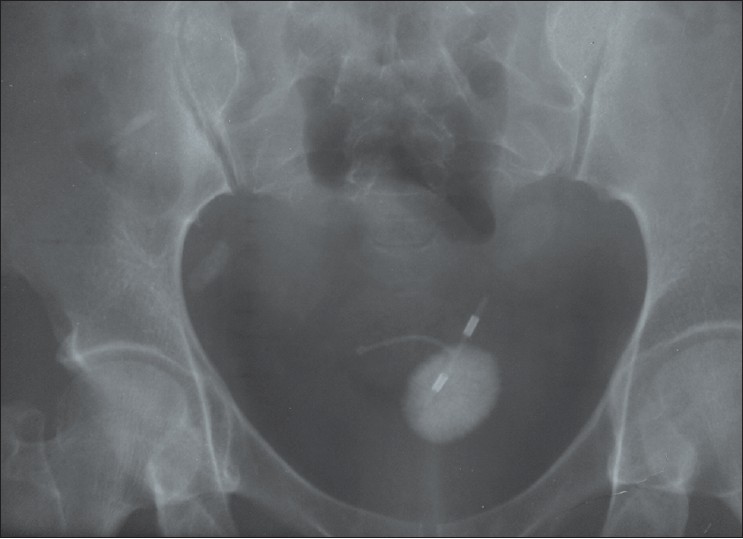  |
Vesical calculus 10 years post missing intrauterine contraceptive device |
p. 48 |
Abdullahi Abdulwahab-Ahmed, Oluwagbemiga Olabisi Ogunleye
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118630 PMID:24470853Intravesical migration of intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD) is rare. Early diagnosis of this rare entity is difficult because of its non-specific manifestations and very low index of suspicion. We present this case of bladder stone following intravesical migration of IUCD found to have been missing since insertion 10 years earlier. Lower abdominal discomfort and a missing vaginal string may be the only pointer to this unfortunate event in the immediate post insertion period. It is pertinent to consider the possibility of an intravesical migration of a missing IUCD in a patient presenting with lower abdominal discomfort, urinary frequency, and missing IUCD string on vaginal examination. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (1) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
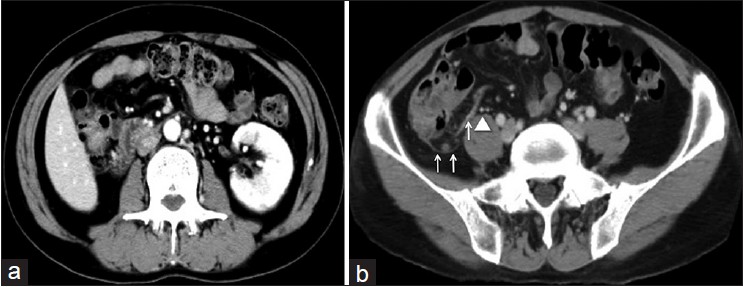  |
Laparoscopic colectomy for a patient with congenital renal agenesis |
p. 51 |
Hiroyuki Tanishima, Tetsuya Horiuchi, Yoshiharu Shono, Masamichi Kimura
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118631 PMID:24470854We present a very rare case of laparoscopic colectomy for a patient with ascending colon cancer and an agenetic right kidney. A 57-year-old man visited our institute for further evaluation for a positive fecal occult blood test. Approximately, 20 years earlier, the right kidney of the patient was found to be congenitally absent. A physical examination indicated no anatomical anomalies in his genitourinary system, and the renal function was within the normal range. Total colonoscopy revealed a cancer of the ascending colon and laparoscopic colectomy was performed. The right colon was mobilized by lateral-to-medial extension of a retroperitoneal dissection between the fusion fascia and the anterior renal fascia. The right testicular vessels were preserved without injury to the anterior renal fascia; however, the right ureter could not be detected. The operation was performed safely. Thus, we believe that in patients with congenital unilateral renal agenesis, the anterior renal fascia is present, and laparoscopic ipsilateral colectomy can be safely performed in such patients. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
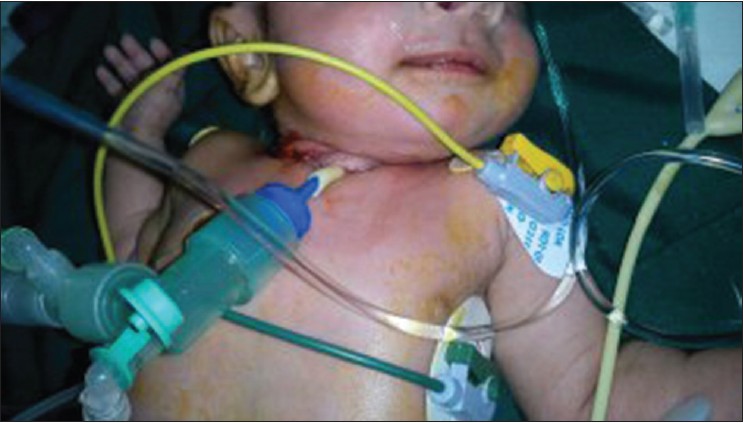  |
The use of t-tube cholangiocatheter stents in the treatment of pediatric tracheomalacia |
p. 54 |
Seyed Mohammad Vahid Hosseini, Mohammad Zarenezhad, Babak Sabet, Mehrdad Malek Shoar, Gholamreza Kangari
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118632 PMID:24470855Tracheomalacia is a common disorder in neonate and infants, which can lead to life-threatening airway occlusion, because of external pressure or intrinsic defect of tracheobroncial cartilage. Aortopexy and Stents are effective in relieving tracheomalacia in the latter patients. In this case we are to show how t-tube cholangiocatheter is effective and easy available in sever tracheomalacia neonates with intrinsic defect. It can be easily replaced and causes no infection, erosion, or sever complication in 9 months period. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
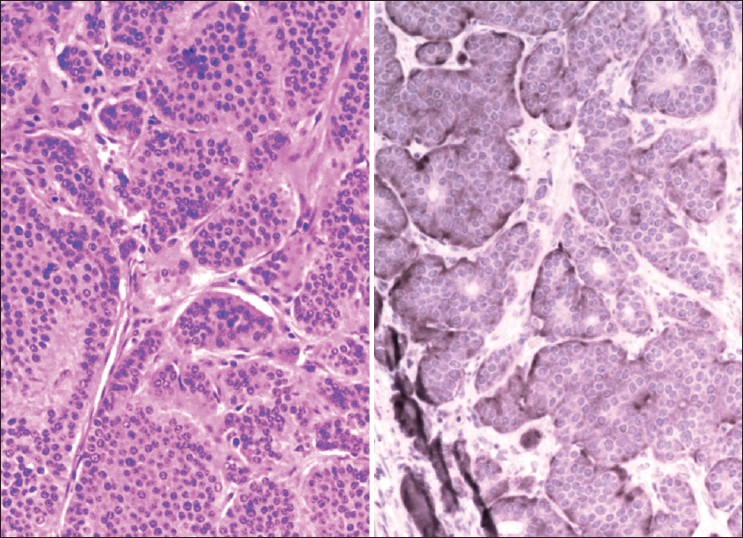  |
Carcinoid tumor in accidental, asymptomatic Meckel's diverticulum |
p. 56 |
Zsolt Baranyai, Valeria Jósa, Keresztely Merkel, Zsofia Zolnai
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118633 PMID:24470856Although Meckel's diverticulum is the most common congenital gastrointestinal disorder, it is controversial whether asymptomatic diverticula in adults should be respected. The authors report the case of a patient who was operated due to ileus caused by adhesions and a Meckel's diverticulum without any sign of inflammation was accidentally noted and removed. As a surprise, the pathological examination of the diverticulum proved carcinoid tumor, a neuroendocrine malignant tumor. The case raises the importance of the removal of asymptomatic Meckel's diverticulum. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| HOW I DO IT |
 |
|
|
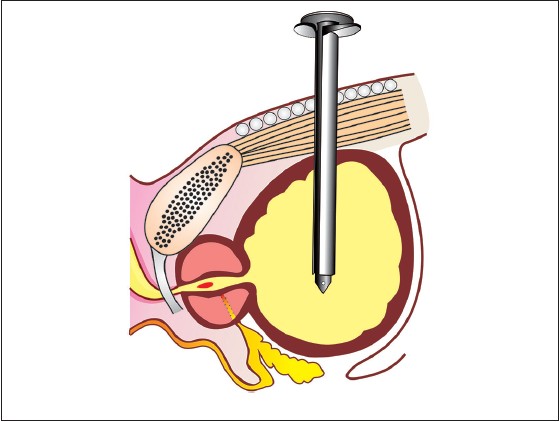  |
Preventing inadvertent placement of foley catheter into prostatic urethra during suprapubic trocar cystostomy: A simple face-saver trick |
p. 58 |
Rahul Yadav, Deepansh Dalela, Divakar Dalela, Rohit Kathpalia, Apul Goel, Satya N Sankhwar
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118634 PMID:24470857During suprapubic cystostomy using standard technique, there always remains a chance of accidental migration of foley catheter through bladder neck into prostatic urethra. We herein present a point of technique in which by keeping the direction of cannula slot toward umbilicus and making it vertical or slightly tilting its tip toward umbilicus during foley placement, prevents the inadvertent migration of catheter into prostatic urethra and further complications. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| LETTERS TO EDITOR |
 |
|
|
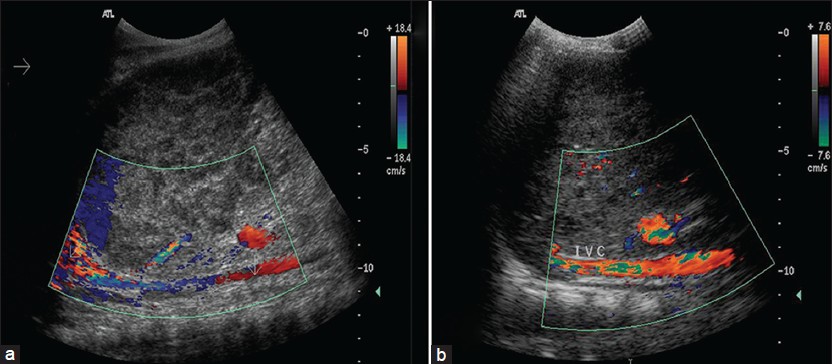  |
Unusual cause of shock: inferior vena cava obstruction complicating pyogenic liver abscess |
p. 60 |
Debajyoti Mohanty, Pankaj Kumar Garg, Bhupendra Kumar Jain, Shuchi Bhatt
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118635 PMID:24470858 |
| [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bimaxillary and bilateral dentigerous cysts: A rare and first reported case |
p. 61 |
Shane J. J. McCrea
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.118636 PMID:24470859 |
| [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|