 |
January-March 2015
Volume 10 | Issue 1
Page Nos. 1-36
Online since Thursday, May 21, 2015
Accessed 11,878 times.
PDF access policy
Journal allows immediate open access to content in HTML + PDF
|
| |
|
|
Show all abstracts Show selected abstracts Add to my list |
|
| ORIGINAL ARTICLES |
|
|
  |
Overall survival of females with breast cancer in the National Cancer Institute, University of Gezira, Sudan |
p. 1 |
Ahmed M Elhaj, AI Abdalsalam, AO Abuidris, AA Eltayeb
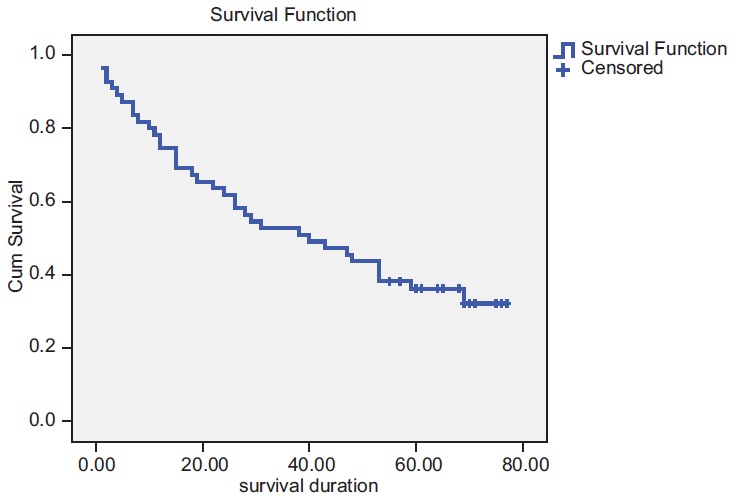
DOI:10.4103/1858-5000.157499 Background: Breast cancer represents 20% of all cancer cases registered in the National Cancer Institute (NCI), University of Gezira, Sudan. New cases of breast cancer presented during the period from January 2001 to December 2001 were included in this study. The objective was to estimate the prognosis of breast cancer in (NCI) in terms of 5 years survival. Methods: The data were collected mainly from the hospital records. In cases of missed data, addresses of kin provided in the hospital records were contacted to find out the survival status of the patients. Data were analyzed according to two sets of variables; patients' related variables and tumor-related variables. Kaplan-Meier method was used to determine the overall survival curve. Results: Totally, 64 patients were evaluated for the study. Of them, 41 (64%) patients presented with disease stage 3 and 4. The mean of follow-up duration was 21.5 months, while the median was 10.5 months. The total number of deaths was 41; those who died in the hospital were 6, representing only 14.6% of the total deaths. The median overall survival period for the population of the study was 40 months and the cumulative survival probability was 38%. Conclusion: The majority of the patients who presented with advanced-stage disease seem to account for the poor overall survival reported in this study. Early detection of breast cancer by breast self-examination and physician breast examination should be encouraged in Sudan to improve treatment results in breast cancer. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comparative measuring between fresh and stored Drabkin's reagent preparations on hemoglobin estimation |
p. 7 |
Nadia Madani, Shamseldein M Ahmed, Tarig Guma, Gad Allah Modawe
DOI:10.4103/1858-5000.157502 This pilot case control hospital base study was conducted to determine the effect of using stored Drabkin's reagent on hemoglobin estimation compared with freshly prepared Drabkin's reagent. Freshly 50 ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid venous blood samples were collected from volunteers from Omdurman Military Hospital, Sudan, the Hb estimation performed using manual method (Hemiglobincyanide or cyanmethemoglobin method), Drabkin's used was prepared in a manner (fresh, 4 days, 8 days and 12 days stored Drabkin's). Then the collected data were analyzed by SPSS computer program. The result shows that the mean concentration of Hb (g/dL) when estimated by prepared Drabkin's reagent for several interval, the fresh reagent result was 13.0 g/dL, 4 days was reagent 11.9 g/dL, 8 days reagent was 11.4 g/dL and 12 days reagent was 11.3 g/dL. The study reveals that the mean of Hb when measured by 4 days stored Drabkin's reagent were statically insignificant and significant when measured by 8 days and 12 days stored Drabkin's reagent (P = 0.05). |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
  |
A comparative study between ropivacaine 30 ml (0.75%) and ropivacaine 30 ml (0.75%) with clonidine 150 μg as an adjuvant in brachial plexus block through supraclavicular approach |
p. 11 |
Shobhana Gupta, Hina Niraj Gadani, HG Thippeswamy
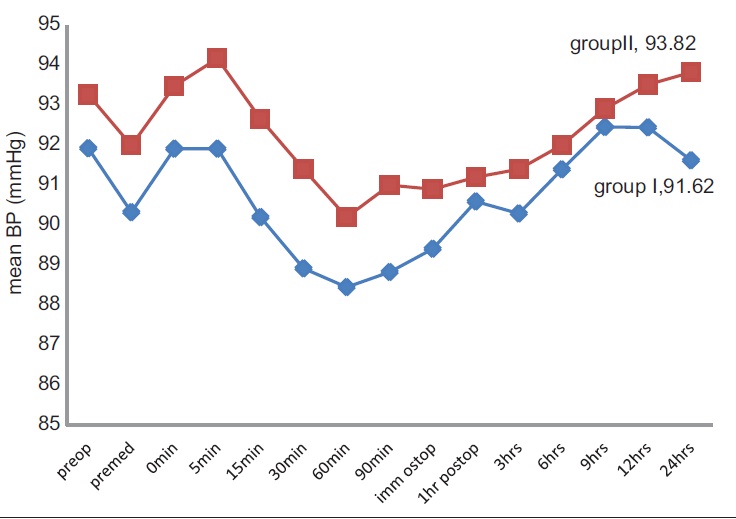
DOI:10.4103/1858-5000.157504 Background: Ropivacaine is a novel alternative to bupivacaine with the less cardiovascular system and central nervous system toxicity. Clonidine, an alpha 2 agonist, may have benefited patients when it is injected at peripheral nerve sites with local anesthetic ropivacaine. Clonidine is second only to epinephrine as a useful adjuvant for brachial plexus blockade. Objective: A clinical study was carried out to compare the anesthetic effects of ropivacaine alone and clonidine as an adjuvant to ropivacaine in brachial plexus block for upper limb surgeries. Materials and Methods: A comparative, double-blind, prospective, randomized, clinical study was carried out on 60 patients of either sex of American Society of Anesthesiologist physical status I and II, with age group 25-65 years undergoing various orthopedic surgeries of upper limb under supraclavicular brachial plexus block. Patients were randomly allocated to either of the two groups of 30 each. Group-R: Injection ropivacaine 30 ml (0.75%) with 1 ml normal saline. Group-ropivacaine clonidine (RC): Iinjection ropivacaine 30 ml (0.75%) with injection clonidine 1 ml (150 μg). Heart rate, mean arterial pressure, onset and duration of motor and sensory blockade were observed during preoperative, intraoperative and postoperative period. At the end of the study, the data were analyzed using Chi-square test for qualitative data and Student t-test. P < 0.05 was considered significant and P < 0.01 was considered as highly significant. Results: Demographic and hemodynamic data were comparable. Onset of sensory and motor block was significantly earlier in Group-R. Duration of analgesia and motor blockade was prolonged in the RC group. Both groups were observed for the side-effects, which were not significant. Conclusions: Addition of clonidine 150 μm to ropivacaine 0.75% 30 ml delays the onset of sensory and motor blockade while prolongs the postoperative motor blockade and analgesia significantly without producing any clinical significant side-effects in brachial plexus block through supraclavicular approach. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| REVIEW ARTICLE |
 |
|
|
|
Incisional hernia management |
p. 17 |
Ismat Mohammed Mutwali
DOI:10.4103/1858-5000.157505 Incisional hernia (IH) is one of the most prevalent postoperative complications of the abdominal surgery. Its recurrence rate is still high in spite of the many techniques and procedures described for the repair of IH and its prevention. The management of IH requires knowledge and expertise to reduce the high rates of postoperative complications and recurrence. The diversity and complexity of IH, may force the hernia surgeon to individualize the treatment, because it seems that there is no universal procedure or technique that can be applied to all type of IHs. The aim of the present review was to provide the surgeons and surgical trainees with updated account on the management of IH. A database search on midline, PubMed and Cochrane database performed to provide comprehensive review. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| CASE REPORTS |
 |
|
|
  |
Hyperpigmentation, a marker of rifampicin overuse in leprosy patient: An incidental finding |
p. 25 |
Pugazhenthan Thangaraju, Hosanna Singh, M Punitha, VC Giri, MK Showkath Ali
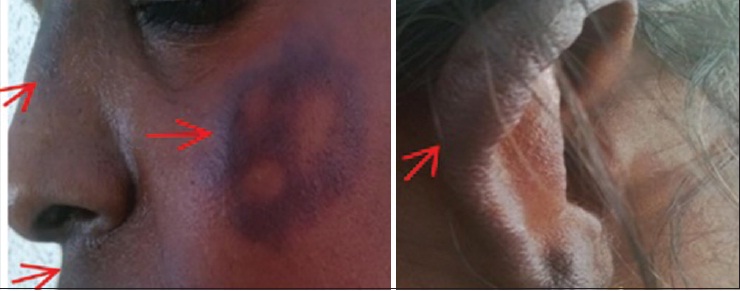
DOI:10.4103/1858-5000.157506 We report an unusual case of hyperpigmentation in a 40-year-old female who was on treatment for leprosy with rifampicin 450 mg daily for 2 months. After scrutinizing the treating physician's previous prescriptions and history, it was found that the patient has never taken clofazimine and minocycline, which were considered to cause hyperpigmentation in antileprosy regimen. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
  |
Schwannoma of the nasal cavity: A case report and a review |
p. 27 |
Esraa M.A. Mosalleum, Vincent M Phillips
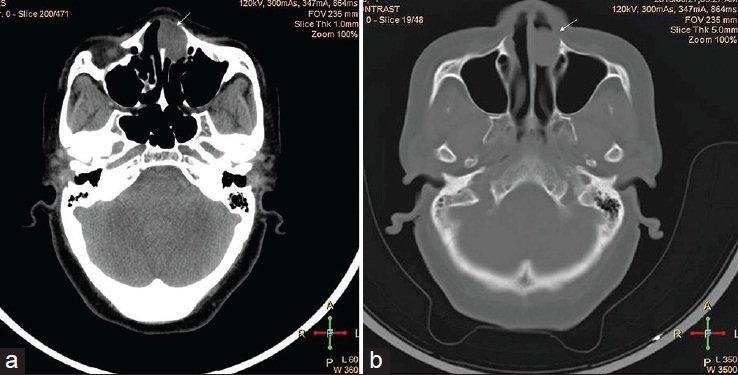
DOI:10.4103/1858-5000.157509 Nasal polyps constitute the clinical presentation of a variety of soft tissue lesions involving the nose. Benign nerve sheath tumors are rare lesions that can present in the nasal cavity. Herein, we present a rare case of nasal schwannoma, and we review the clinical and the radiological features of cases published as nasal cavity schwannoma in the English literature. Extensive PubMed search revealed only 17 cases of schwannoma of the nasal cavity reported during the period 2000-2013. The mean age of presentation was 39 years, and a female predilection was observed. The main radiological feature was a homogenous well circumscribed mass on plain radiography with intermediate intensity on T1-weighted and T2-weighted and homogenous enhancement on contrast magnetic resonance imaging. No invasive growth pattern or cranial extension was reported. The histological features of nasal cavity schwannomas were similar to their soft tissue counterparts. The literature shows that malignant cases are rare. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
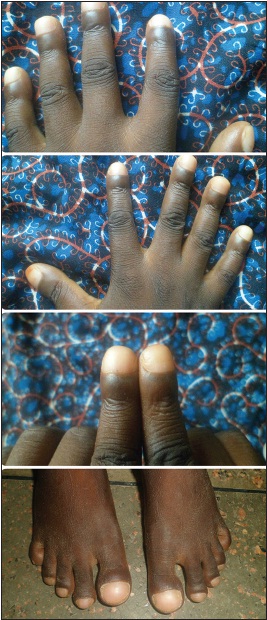  |
Childhood pulmonary tuberculosis with digital clubbing |
p. 31 |
Ibrahim Aliyu, Zainab Ibrahim
DOI:10.4103/1858-5000.157510 Tuberculosis is prevalent in the tropics and sub-tropics; late treatment may result in severe morbidity and mortality. Digital clubbing has been associated with several diseases including pulmonary tuberculosis though the exact mechanism is poorly understood; this has been linked mostly with severe adult pulmonary tuberculosis associated with cavitations, hypoalbuminemia and smear-positive sputum, but the case of an 11-year-old boy who presented with digital clubbing and leukonychia with absence of cavitary lesion or hypoalbuminemia is reported. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| LETTER TO EDITOR |
 |
|
|
|
Strategies to ensure gender equality in the health sector |
p. 35 |
Saurabh RamBihariLal Shrivastava, Prateek Saurabh Shrivastava, Jegadeesh Ramasamy
DOI:10.4103/1858-5000.157513 |
| [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|