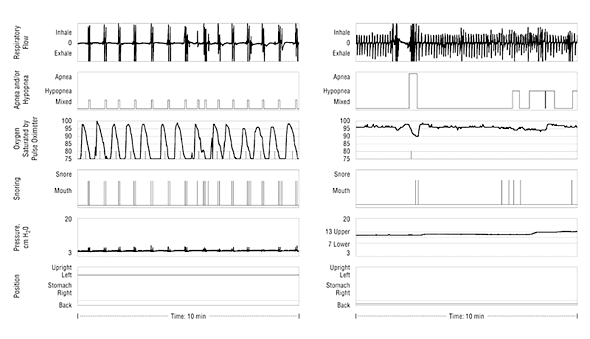
Figure 1. Left, Ten-minute segment of the analog printout from a study subject with severe sleep apnea diagnosed using the automatic titrating continuous positive airway pressure machine (Horizon; DeVilbiss, Somerset, Pa) and dedicated computer (Surveyor; DeVilbiss) as an unattended monitor for apnea and/or hypopnea. Panel 1 (top most) shows airflow from the pneumotachograph with repetitive apneas interspersed between 2 and 3 breaths; panel 2, machine scoring of apneas; panel 3, the repetitive oxyhemoglobin desaturation related to these apneas; panel 4, repeated episodes of severe snoring; panel 5, the continuous positive airway nasal mask pressure at 3 cm H20, which allows the pneumotachograph to function; and panel 6, body position. Right, The same patient studied on a subsequent night with the automatic titrating continuous positive airway pressure machine placed in the titration mode. The parameters on each panel are the same as on the left. The automatic titration upper and lower nasal mask pressure limits were set at 13 and 7 cm H2O, respectively. There was marked attenuation of apneas seen in panel 1, with normalization of arterial oxygen saturation. Panel 5 shows the nasal mask pressure being titrated upward to 13 cm H2O in response to snoring and a single apnea seen in panel 1. The subject is sleeping supine in both studies.