
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
The GoLoco Motif: Heralding a New Tango Between G Protein Signaling and Cell Division
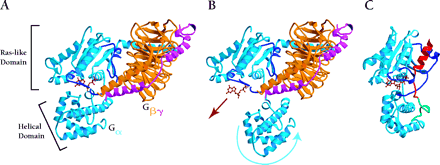
Proposed mechanism for GoLoco-mediated GDI activity. A. In the Gαβγ heterotrimer, Gβγ subunits (orange and magenta, respectively) contact Gα (light blue) through the Ras-like domain and the associated switch regions (dark blue). GDP (brown) is not contacted by Gβγ, but is held tightly by the Gα subunit. B. GPCR activation is thought to change the orientation of the all-helical domain relative to the Ras-like domain (movement indicated by blue arrow), thus loosening Gα's grip on the nucleotide and allowing it to dissociate (brown arrow) (23). C. The GoLoco peptide acts as a Gα clamp by restricting movement of the two Gα domains relative to one another. The conserved nineteen-residue GoLoco motif (red) binds to the Ras-like domain and the switch regions while the C-terminal extension (green) stabilizes the all-helical domain. Atomic coordinates of Gαβγ taken from 1GOT.


