
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
The Choline Transporter Resurfaces: New Roles for Synaptic Vesicles?
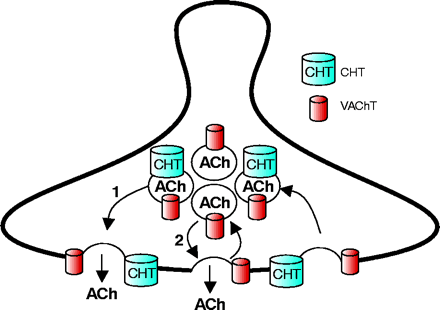
Localization of CHT to a subset of synaptic vesicles couples plasma membrane delivery of CHT to the rate of ACh release. Although CHT functions at the plasma membrane to capture choline for ACh synthesis, recent results indicate that it is also abundantly localized to a subset of VAChT-positive, ACh-containing synaptic vesicles (66). Thus, ACh release occurs by the fusion of two distinct but equally abundant subsets of synaptic vesicles, one that contains both CHT and VAChT and a second class of vesicles containing only VAChT. At steady state in presynaptic terminals, no major pools of CHT exist on VAChT-negative vesicles; therefore, ACh release and CHT insertion into the plasma membrane are very intimately linked.


