
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Looking at Lithium: Molecular Moods and Complex Behaviour
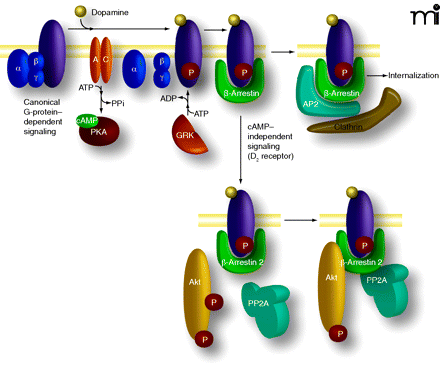
Dual role of β–arrestins in mediating GPCR desensitization and G protein–independent signaling. Activation of dopamine receptors (DAR) activates G proteins, which leads to activation (Gαs) or inhibition (Gαi/o) of adenylyl cyclase and modulation of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase PKA (G protein–dependent signaling). This is rapidly followed by receptor phosphorylation by GRKs and the recruitment of β–arrestins, leading to termination of G protein signaling and formation of an internalization complex formed by β–arrestin 1 and/or β–arrestin 2, AP2, clathrin. Recruitment of β–arrestin 2 following activation of D2-class receptors also results in the formation of a signaling complex composed at least of β–arrestin 2, PP2A, and Akt, which results in a deactivation of Akt by PP2A and subsequent stimulation of GSK3-mediated signaling.


