
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Proteases Display Biased Agonism at Protease-Activated Receptors: Location matters!
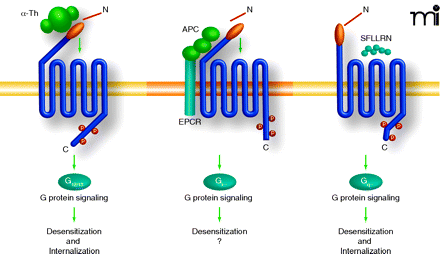
Differentially activated PAR1 is regulated by distinct mechanism. Thrombin, APC, and peptide agonists promote distinct PAR1 signaling in endothelial cells, suggesting that distinct active receptor conformations are induced. The mechanisms responsible for PAR1 desensitization following activation by distinct proteases appears be different. Activation of PAR1 by thrombin, peptide agonist, and APC promote rapid and robust receptor phosphorylation, an event critical for uncoupling PAR1 from G-protein signaling. The kinases that mediate PAR1 phosphorylation and PAR1 phosphorylation sites induced by the distinct ligands, however, have not been thoroughly examined. Moreover, thrombin and peptide agonist but not APC promotes PAR1 internalization, suggesting that the different active receptor conformations have the capacity to differentially engage the endocytic machinery. The role of arrestins or other endocytic adaptors proteins in regulating distinctly activated PAR1 internalization has not been examined.


