 |
July-December 2013
Volume 5 | Issue 2
Page Nos. 65-115
Online since Thursday, March 13, 2014
Accessed 26,566 times.
PDF access policy
Full text access is free in HTML pages; however the journal allows PDF access only to users from NIGERIA, developing countries and paid subscribers.
EPub access policy
Full text in EPub is free except for the current issue. Access to the latest issue is reserved only for the paid subscribers.
|
| |
|
|
Show all abstracts Show selected abstracts Add to my list |
|
| ORIGINAL ARTICLES |
|
|
  |
Facial fracture management in Northwest Nigeria |
p. 65 |
Abdurrazaq Olanrewaju Taiwo, Olujide Oladele Soyele, Ndubuizi Ugochukwu Godwin, Adebayo Aremu Ibikunle
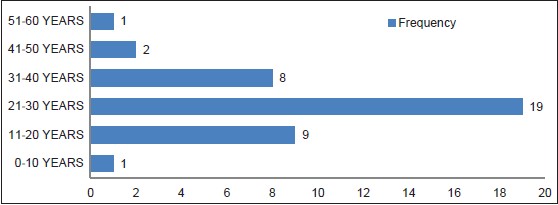
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.128723 PMID:24741422Background: Facial fracture is gradually become a public health problem in our community due to the attendant morbidity and mortality. Hence, the aim of this study was to determine the pattern of facial fracture in Dental and Maxillofacial Surgery Department of Usmanu Danfodiyo University Teaching Hospital. This cross-sectional study was undertaken to provide information regarding gender, age, etiology, and diagnosis of patients with maxillofacial fractures. Materials and Methods: A 1-year review of patients diagnosed and treated for facial fractures in Usmanu Danfodiyo University Teaching Hospital between January 2011 and December 2011. The diagnosis was based on radiographic data and clinical examination. The main analysis outcome measures were etiology, age, gender, site, and treatment. Data were organized and presented by means of descriptive statistics and Pearson's Chi-square test. The level of significance adopted was 5%. Results: A total of 40 patients were treated in this period. Over 95% were male, 81% were caused by road traffic crash (RTC) and 86.4% were in the 21-30 years group. Most patients (52%) had mandibular fractures, and the most common site was the body. Most patients with midfacial fractures had fractures of the zygomaticomaxillary region (36%), while fractures of the parasymphyseal region were more common in the mandible 156 (31%). The most common treatment for jaw fractures was mandibulomaxillary fixation (MMF). Stable zygomatic complex fractures were reduced (elevated) intraorally, and unstable ones were supported by antral packs. Conclusions: This study highlights facial fractures secondary to RTC as a serious public health problem in our environment. Preventive strategies remain the cheapest way to reduce direct and indirect costs of the sequelae of RTC. It also bring to the fore the necessity to shift to open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) of fractures. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
  |
Pseudocyst of pinna and its treatment with surgical Deroofing: An experience at tertiary hospitals |
p. 72 |
Nazir A Khan, Mudasir ul Islam, Ayaz ur Rehman, Shakeel Ahmad
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.128728 PMID:24741423Introduction: Pseudocyst of pinna is an uncommon condition hardly encountered in routine ENT practice. The involvement is usually seen in scaphoid, triangular fossa, and antihelix. Medical treatment is ineffective. Various treatments are suggested in the literature. The aims of the paper were to study the clinical characteristic of patients with pseudocysts and to share our experience with surgical deroofing and buttoning as a definitive treatment. Materials and Methods: Twenty-six patients were diagnosed with pseudocyst of the auricle between April 2011 and 2013 in two medical college hospitals. Clinical characteristics were noted. All patients underwent incision and drainage with removal of anterior cartilage leaflet followed by buttoning for 12 days. Results and Observations: Out of 26 patients, only two were females. Involvement of left side was seen more than right one. None had bilateral involvement. Adults in the age group of 31-40 were commonly affected. Most common site of involvement was scaphoid and triangular fossa. The success rate with primary I and D and buttoning was 96%. Conclusions: Pseudocyst of the pinna is a benign condition of unknown etiology affecting the pinna, commonly encountered in middle-aged men. Many modalities of treatment have been recommended in the literature with varied recurrence and failure rates. The best form of treatment with minimum recurrence is incision and drainage with removal of anterior cartilage leaflet with buttoning. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| CASE REPORTS |
 |
|
|
  |
Loss of guide wire: A lesson learnt review of literature |
p. 78 |
Rajiv Srivastav, Vishal Yadav, Dimpy Sharma, Vikas Yadav
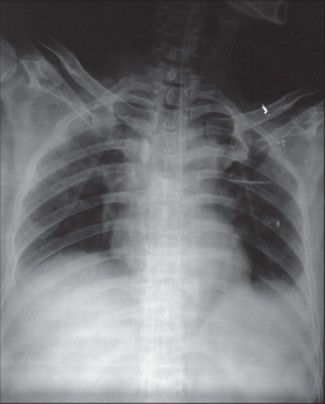
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.128732 PMID:24741424Catheterization of central veins is a routine technique which is widely used in emergency department and medical intensive care units. Seldinger's technique is widely used to place central venous and arterial catheters and is generally considered safe. The technique does have multiple potential risks. Guide wire-related complications are rare but potentially serious. We describe a case of a lost guide wire during central venous catheter (CVC) insertion followed by a review of the literature of this topic. Measures which can be taken to prevent such complications are explained in detail as well as recommended steps to remedy errors should they occur. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (3) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
  |
Isolated pancreatic metastasis from malignant melanoma: Is pancreatectomy worthwile? |
p. 82 |
David Jérémie Birnbaum, Vincent Moutardier, Olivier Turrini, Anthony Gonçalves, Jean Robert Delpero
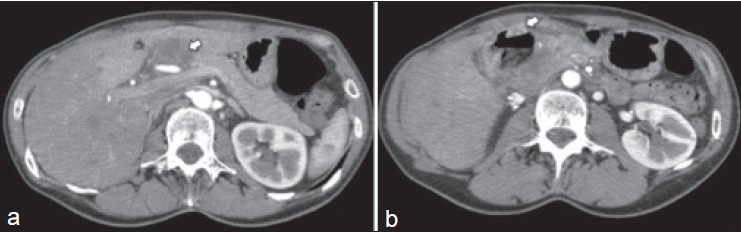
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.128733 PMID:24741425Isolated pancreatic metastasis from malignant melanoma (IPMMM) is rare because most melanoma patients already have a widespread disease at diagnosis. No adjuvant systemic treatment is known to be efficient in this setting. Experience with pancreatic resection for IPMMM is limited and controversial. We report here the case of an IPMMM patient successfully treated by pancreaticoduodenectomy with a prolonged survival of 6 years. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (1) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
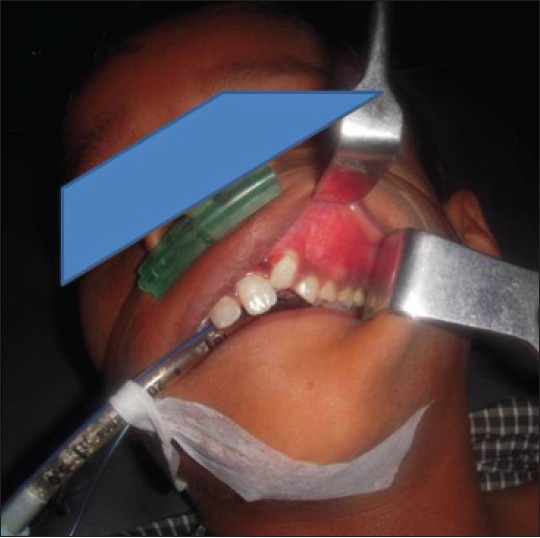  |
Dentigerous cyst associated with ectopic canine and a supernumerary tooth: A rare occurrence |
p. 85 |
Ashwini Ramakrishna, Pravin Lambade
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.128738 PMID:24741426Amongst the cysts of the jaw dentigerous cyst (DC) is one of the most prevalent types of odontogenic cysts, which is associated with the crown of an unerupted or developing tooth. DC is more commonly seen with mandibular third molar and maxillary canine and rarely other teeth are involved. These cysts seldom associate with supernumerary teeth. The purpose of this article is to describe a case of large dentigerous cyst associated with supernumerary teeth and an ectopic canine, which is a rare presentation along with its management. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
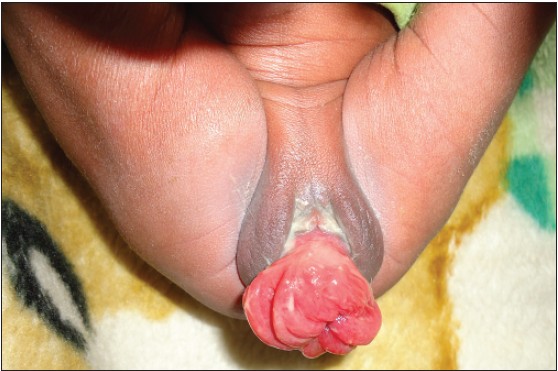  |
Congenital uterovaginal prolapse present at birth  |
p. 89 |
Ekwunife Okechukwu Hyginus, Chukwuka Onuora John
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.128741 PMID:24741427Uterovaginal prolapse presenting at birth is very rare. The cause is attributed to conditions that can cause poor innervation or weakness of the pelvic floor muscle and the supporting ligaments. Different methods of treatment have been used in the past to reduce and maintain reduction of the prolapse. We report a case of a congenital UVP in a day old child noticed at delivery. He was delivered breech and had a sacral dimple with a tuft of hair. He was successfully managed conservatively with digital reduction and strapping of the buttocks down to the legs with crepe bandage for 72 h. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (1) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
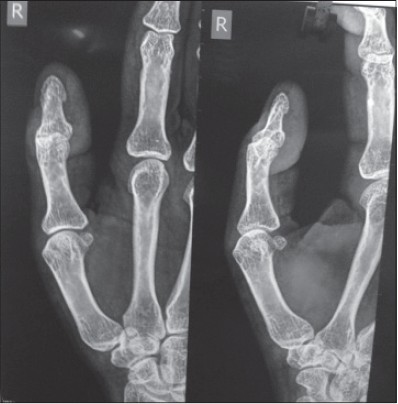  |
Glomus tumor of thumb occurring at unusual location |
p. 92 |
Samir Dwidmuthe, Amit Nemade, Santhosh Rai
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.128745 PMID:24741428Glomus tumour are painful swelling arising from glomus bodies. They are very rare in occurrence. Most of the time the presenting symptoms is severely painful fingertip without palpable swelling. Their most common location is the subungual region of digits. We report the rare case of a glomus tumour located in an uncommon location, i.e., at the tip of right thumb medial aspect near to tendon attachment. The peculiarity of this lesion is that this lesion on magnetic resonance imaging was found to arise from the insertion of flexure pollicis longus tendon and was reported as synovial swelling arising from tendon sheath. Clinical findings were consistent with glomus tumour. Excision biopsy confirmed diagnosis of glomus tumour. Although rare, glomus tumour should be considered as differential diagnosis for fingertip pain and excision of lesion gives complete pain relief. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
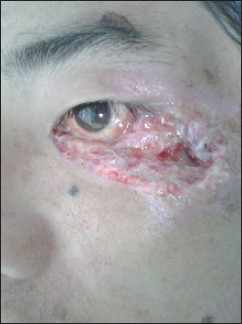  |
Total reconstruction of lower eyelid in a post-traumatic patient using modified fricke's cheek flap |
p. 95 |
Subhabrata Sengupta, Binayak Baruah, Suvra Pal, Isha Preet Tuli
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.128749 PMID:24741429Eyelids are very complex structure, reconstruction of which is a challenge to surgeons. Reconstruction of eyelids may be required in a variety of conditions like congenital anomalies, trauma, or postsurgical excision in malignant lesions involving the eyelids. There are numerous ways to reconstruct the eyelids; the best procedure depends on both the skill of the surgeon and the condition of the patient. Fricke' lateral temporal based flap was first described in 1829 for reconstruction of the eyelids and lateral canthal region. This flap had inherent problems regarding cosmetic appearance of the eyebrows. The modified Fricke's flap based on the cheek has the advantage of avoiding such complications. It is very easy and rapid outpatient department (OPD) based procedure with acceptable cosmetic and functional result. It can be done by all ear, nose, and throat (ENT) and head and neck surgeons without any reconstructive training. In this article we are presenting a case of total reconstruction of lower eyelid using the modified Fricke's cheek flap. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
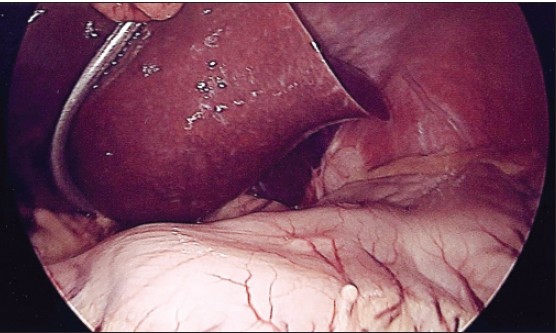  |
Successful laparoscopic removal of an ingested toothbrush |
p. 99 |
Karim Jamal, Shalin Shaunak, Sarandeep Kalsi, Dhiren Nehra
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.128751 PMID:24741430Most ingested foreign bodies will pass through the gastrointestinal tract without any problems. On the other hand long, slender objects such as a toothbrush will rarely be able to negotiate the angulated and fixed retroperitoneal duodenal loop. Spontaneous toothbrush passage has never been described and therefore endoscopic or surgical removal is always required. Here we describe an asymptomatic young female presenting to out-patient clinic with a history of unintentional toothbrush ingestion 4 years prior. Endoscopic removal was unsuccessful because the toothbrush was partially embedded in to the gastric mucosa. We describe the second case to date of laparoscopic removal of a toothbrush via a gastrotomy with subsequent intra-corporeal repair of the defect. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
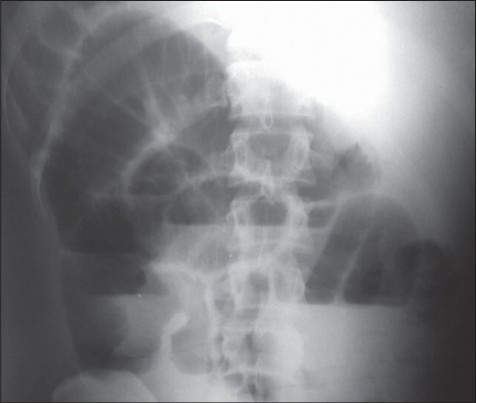  |
Axial torsion of gangrenous Meckel's diverticulum causing small bowel obstruction |
p. 103 |
K Sasikumar, Ravinder Naik Noonavath, GS Sreenath, Nanda Kishore Maroju
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.128752 PMID:24741431Meckel's diverticulum (MD) is a commonly encountered congenital anomaly of the small intestine. We report an extremely unusual case of an axially torted, gangrenous MD presenting as acute intestinal obstruction. A 26-year-old male patient presented to our emergency department with 3 days history of abdominal pain, distention and bilious vomiting. On laparotomy, there was minimal hemorrhagic fluid localized in right iliac fossa and small bowel loops were dilated. A MD was seen attached to the mesentery of nonadjacent small bowel by a peritoneal band. The diverticulum was axially torted and gangrenous. In addition, there was compression of ileum by the peritoneal band resulting in intestinal obstruction, which was relieved on dividing the band. Resection and anastomosis of the small bowel including the MD was performed. We hereby report a rare and unusual complication of a MD. Although treatment outcome is generally good, pre-operative diagnosis is often difficult. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (1) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
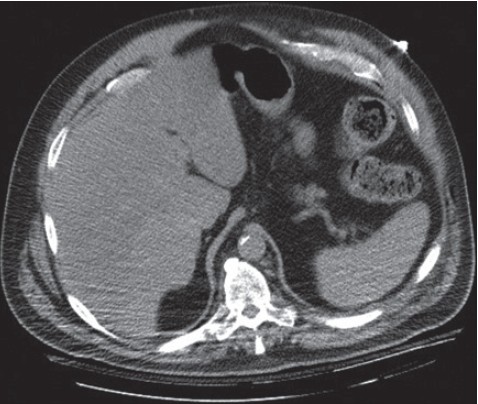  |
Clinicoradiological diagnosis of cough-induced intercostal hernia |
p. 106 |
Andrew Dobradin, Jessica Bello
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.128754 PMID:24741432Cough-induced intercostal hernias without any type of external trauma are very uncommon. There have been less than 10 cases documented in literature. This clinical report describes a 66-year-old male who developed an intercostal hernia induced by a severe cough due to bilateral pneumonia and a subsequent rib fracture. It took almost a full year to diagnose this patient's chest wall mass. Only after taking careful history and reviewing all the images, the diagnosis of intercostal hernia was made. He was referred to a cardiothoracic surgeon for treatment. Intercostal hernias can be caused by the sheer exertion of coughing without any prior history of trauma to the chest wall or abdomen. Early diagnosis is difficult and had to be based on clinical signs and symptoms. The imaging studies might help to establish diagnosis, but cannot replace a diligent examination and clinical interview. The treatment of the chest wall defect is case dependent. Surgical repair reinforcement of the intercostal muscles might be required with prosthetic nonabsorbable (polypropylene) mesh. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| HOW I DO IT |
 |
|
|
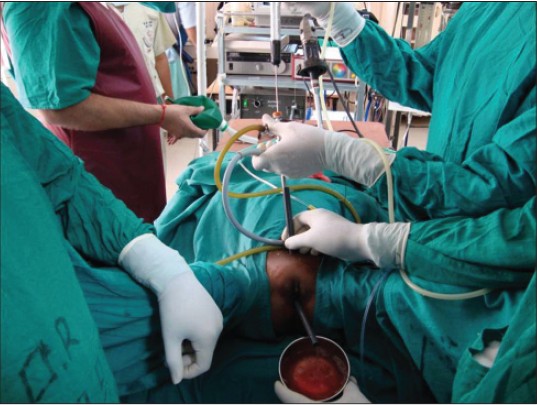  |
The twin amplatz sheath method: a modified technique of percutaneous cystolithotripsy for large bladder stones in female patients |
p. 109 |
Amit Kumar, Deepansh Dalela, Divakar Dalela, Apul Goel, Sagorika Paul, Satya N Sankhwar
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.128757 PMID:24741433To minimize the operative time and to avoid open cystolithotomy in women with large bladder stone (>5 cm), we present here a modification of percutaneous cystolithotomy, a well-described standard procedure for urinary bladder stones. With this technique, suprapubic percutaneous access was achieved under cystoscopic guidance. The suprapubic tract was dilated and an Amplatz sheath of 30 Fr was placed. Simultaneously, the urethra was sequentially dilated with fascial dilators and a 28 Fr Amplatz sheath was guided into the bladder and the foot end of the table lowered to 20° to facilitate high-speed outflow of irrigant and stone particles. A 26.5 Fr nephroscope was passed through the suprapubic Amplatz sheath and the stone was fragmented by intracorporeal pneumatic device keeping the stone close to the proximal end of the urethral Amplatz. These maneuvers help in washing out stone fragments periurethrally and keeping the endoscopic vision clear while breaking the stone. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (1) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| COMMENTARY |
 |
|
|
|
Twin amplatz sheath method: a modified technique of percutaneous cystolithotripsy for large bladder stone in females |
p. 111 |
Athanasios Papatsoris
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.128755 PMID:24741434 |
| [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (1) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| HOW I DO IT |
 |
|
|
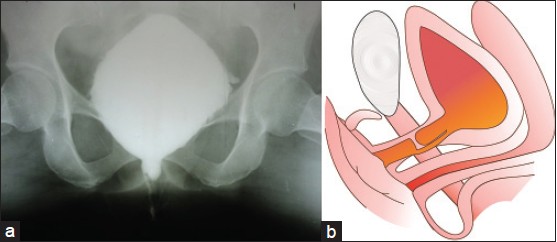  |
Anastomotic Urethroplasty in Female Urethral Stricture Guided by Cystoscopy - A Point of Technique |
p. 113 |
Sachin Patil, Deepansh Dalela, Divakar Dalela, Apul Goel, Pushpalata Sankhwar, Satya N Sankhwar
DOI:10.4103/2006-8808.128758 PMID:24741435Purpose: During anastomotic urethroplasty for stricture urethra with false passage using standard technique, there remains a chance of anastomosis of normal distal urethra to proximal false lumen. Herein, we present a point of technique in which by using antegrade cystoscope, one cannot just identify and dissect normal anatomical proximal urethral lumen, but also perform some of the steps for anastomosis under direct vision. This will avoid making anastomosis to false lumen and thus leading to further complications. Materials and Method s : We report a case of 35-years-female who was presented to us with total mid-urethral stricture with false passage following multiple urethral dilatation attempts. We used antegrade cystoscopy during anastomotic urethroplasty to identify and dissect the proximal end of urethra thereby avoiding anastomosis to false tract. Results: We successfully performed anastomotic urethroplasty avoiding false passage. Post-operative Uroflow showed Q max of 18 ml/sec. Voiding cystourethrogram post-operatively showed anastomosis between normal anatomical lumens. Conclusion: This modification of using antegrade cystoscopy helps to identify proximal urethral end which in turn helps in avoiding anastomosis to false tract and ensures anastomosis between normal lumens. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|